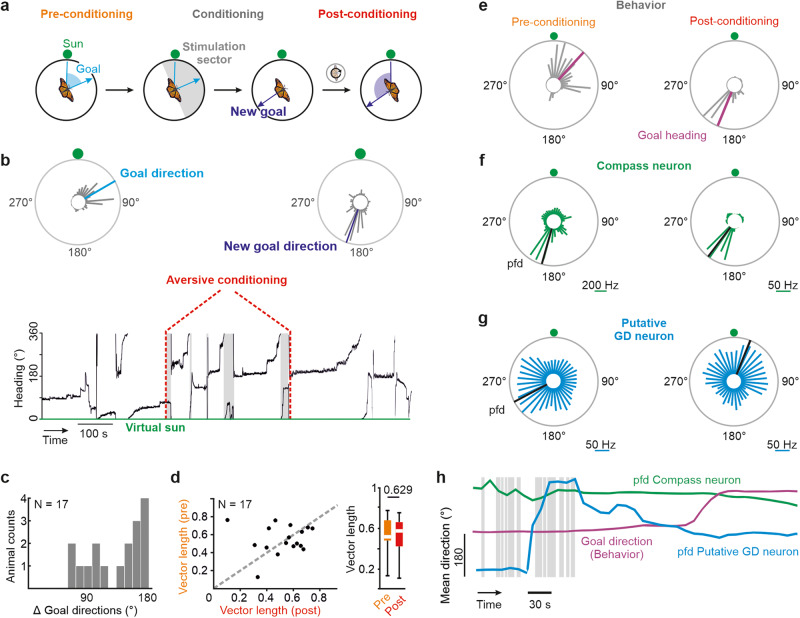
Fig. 2. Resetting the goal direction.
a Schematic drawing of how the butterfly’s goal direction was reset. For pre-conditioning, the butterfly oriented with respect to the virtual sun. During conditioning, we applied electric shocks to the butterfly’s neck whenever it headed in its initial goal direction (±90°; stimulation sector). After several electric shocks, we expected that the butterfly sets a new goal direction with respect to the virtual sun. b (Top) Circular histograms summarizing the heading (gray bars) of one representative butterfly before (left circular plot) and after conditioning (right circular plot). Respectively, blue and violet lines indicate the initial and new goal direction of the butterfly. (Bottom) Heading (black) plotted as a function of time. Gray boxes highlight periods of electric shocks. The virtual sun was located at 0°. c Changes in goal directions induced by aversive conditioning in 17 butterflies. d Vector lengths (flight directedness) compared between pre- and post-conditioning (p = 0.63, R2 = 0.015, N = 17, two-sided paired t-test). Each dot represents the mean vector length of one butterfly. Box plots indicate median (middle line), 25th, 75th percentile (box) and 5th and 95th percentile (whiskers). e Circular histograms summarizing the heading of one representative butterfly before (pre-conditioning) and after (post-conditioning) conditioning. Magenta lines indicate the goal heading (mean heading). f, g Angular tuning of a compass neuron (green) and a putative GD neuron (blue) corresponding to the flight directions presented in (e). Black lines indicate the neurons’ pfds. h Goal direction (magenta), pfds of a compass (green), and putative GD neuron (blue) plotted as a function of time. Gray boxes highlight periods of electric stimulation. The first data point on the x-axis represents the value measured during pre-conditioning. Notably, the pfd of the compass neuron was relatively invariant compared to the pfd of the putative GD neuron. The pfd of the putative GD neuron began to shift before the butterfly changed its goal direction. Source data file: datasource.xlsx Fig. 2.