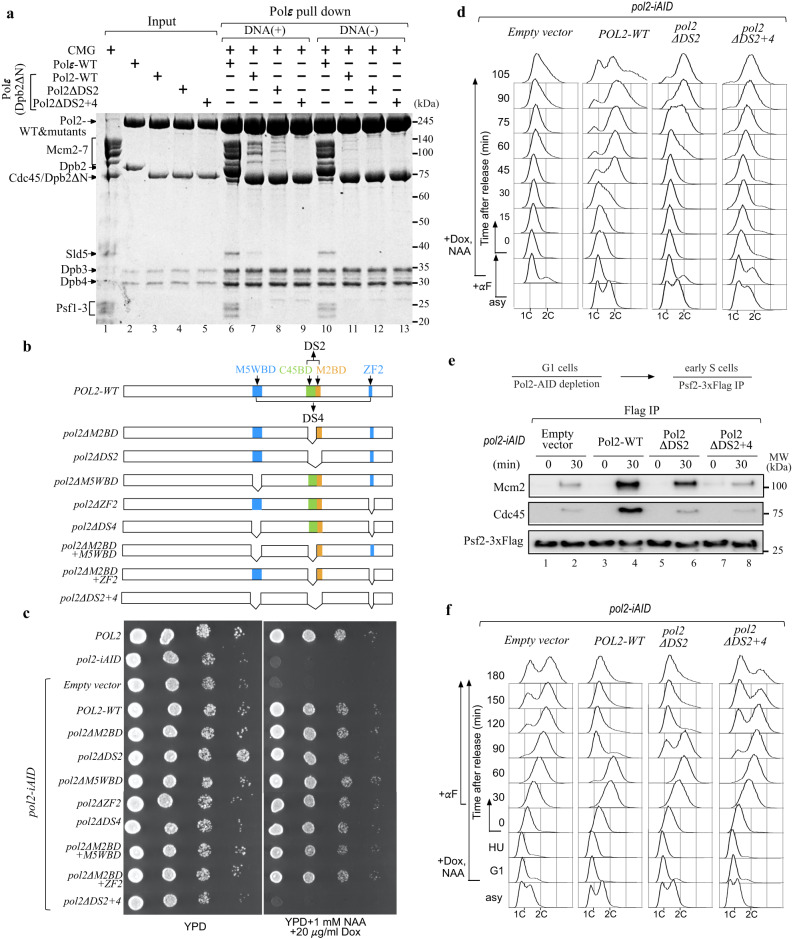
Fig. 2. The physiological function of Polε-MCM coupling in replication initiation and S phase progression.
a In vitro CMG pulldown assays to examine the binding affinity of Polε, PolεΔ2N, and the related mutants (Pol2ΔDS2 and Pol2ΔDS2+4) to CMG in the presence or absence of DNA. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments. b Schematic illustration of pol2 mutant construction. c Polε-MCM coupling is essential for cell viability. The indicated truncation mutants of Pol2 were tested for complementation of a depletion of Pol2-AID, the expression of which is under the control of Tet promoter. YPD: yeast extract-peptone-dextrose, NAA: 1-naphthalene acetic acid, Dox: doxycycline. d Flow cytometry profiles of cells collected from the α factor block-and-release assays with the indicated pol2-iAID strains under restrictive conditions. e The lysates of the indicated samples were prepared for Flag IP with anti-FLAG beads. Each sample was analyzed with antibodies against Flag, Cdc45, and Mcm2. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments. Source data are provided as a source data file. f Flow cytometry profiles of cells collected from the hydroxyurea (HU) block-and-release assays. α factor was added after cells were released from HU arrest.