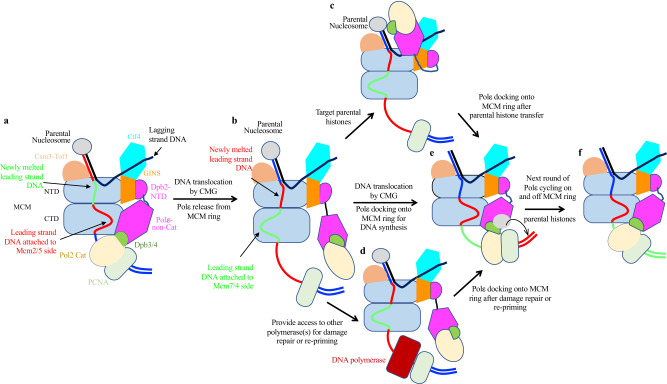
Fig. 7. Model illustrating potential functions of Polε cycling on and off MCM ring.
a Polε binding to the MCM ring facilitates its engagement with the PCNA-DNA complex to drive strand extension. b DNA translocating away the Mcm2:5 interface releases Polε from MCM. c Polε flips over CMG helicase to target parental histones via Dpb3-4 for redisposition of epigenetic information from parental DNA strand to newly synthesized leading strand. d Upon DNA damage, a flexible Polε can provide access to other polymerases for damage repair and/or re-priming for fork restart. e Leading-strand DNA relocating to the Mcm2:5 interface enables Polε binding to MCM to re-establish strand extension. f DNA translocation by CMG initiates a new round of Polε cycling on and off the MCM ring.