Figure 1.
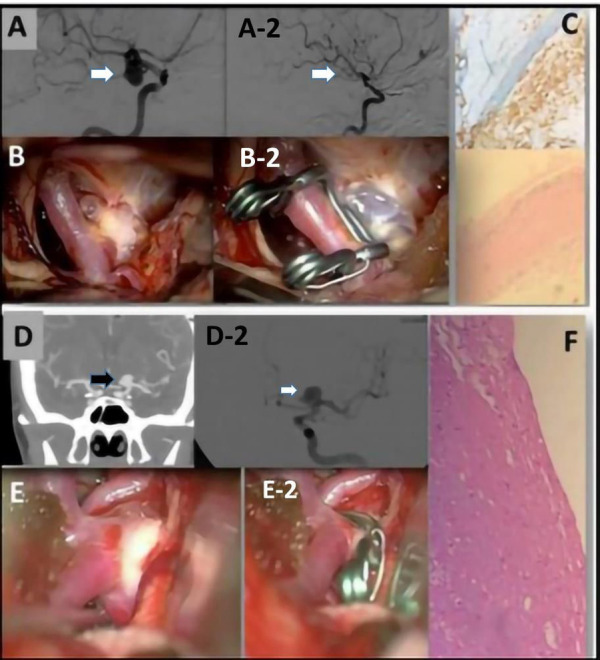
(A) A preoperative evaluation of an ICA aneurysm with a DSA. (A-2) A postoperative evaluation after clipping of the previous ICA aneurysm. (B) Image obtained with a surgical microscope of the intracranial aneurysm (IA). (B-2) Postoperative image obtained with a surgical microscope of the IA after clipping. (C) Representative examples of H&E staining performed on IA domes directly fixed in formalin. The aneurysm wall is characterized by fibrosis and foam cells. CD68+ foam cells. (D) A preoperative CTA image of a left ICA aneurysm and (D-2) a DSA evaluation of the same aneurysm. (E) Intraoperative view of the IA obtained before clipping and (E-2) obtained after the clipping. (F) Increase of the ECM associated with widespread rarefaction of the muscular component. In the adventitia, there is also lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate and granulocytes.
