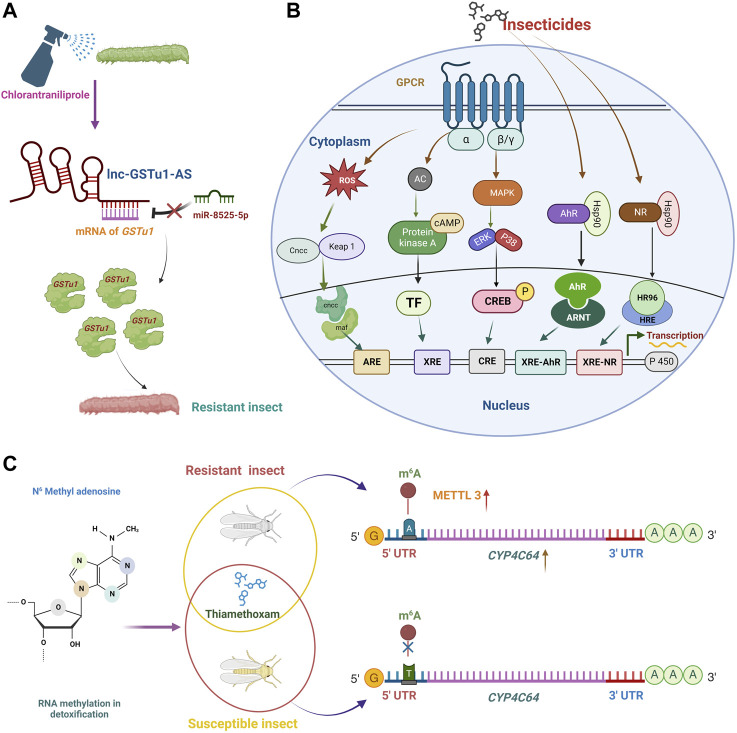
FIGURE 5.
The regulation of insecticide resistance mechanisms involves epi-transcriptome signals, detoxification signaling pathways, and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). (A) lncRNAs influence miRNA-mediated insecticide resistance regulation. Regulation mechanisms include lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA interaction and lncRNA-mediated regulation of miRNA expression. GSTu1, a detoxifying gene, is involved in the chlorantraniliprole resistance of P. xylostella. A long non-coding RNA, lnc-GSTu1-AS, interacted with GSTu1 by forming an RNA duplex, masking the binding site of microRNA, miR-8525-5p, at the GSTu1-3′ UTR. lnc-GSTu1-AS maintained the mRNA stability of GSTu1 by preventing its degradation, which could have been induced by miR-8525-5p and thus resulting in increased production of detoxification gene (GSTu1), increased the resistance of P. xylostella to chlorantraniliprole. (B) Detoxification enzyme induction pathway. This pathway involves upregulating detoxification enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 monooxygenases, esterases, and glutathione S-transferases. They are the CncC/Keap1, NR, PKA, MAPK/CREB, and AhR/ARNT pathways. The activated molecules of these pathways, such as Cncc/maf, TF, CREB, Ahr/AHRNT, and HR96/HRE, respectively, in the cytoplasm, interact with their corresponding response element in the nucleus to regulate the expression of detoxification genes through transcription. The arrows indicate the cascade of effectors in the signaling pathway. (C) N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is a modified form of adenosine widely involved in gene expression regulation. Mutation (T to A at position-206 bp) was observed in the 5′UTR of CYP4C64 that was observed at a much greater frequency in the thiamethoxam-resistant strains compared with the susceptible strain. The T at 206 bp helps bind m6A, and the overexpression of the enzyme METTL (methyltransferase) led to the development of thiamethoxam-resistant insects. CncC, Cap‘n’ Collar isoform C; Maf, Musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma; ARE, Antioxidant responsive element; Gas, G protein alpha unit which stimulates adenyl cyclase; AC, adenyl cyclase; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PKA, protein kinase A; TF, Transcription factor; XRE, xenobiotic response element; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK, extracellular regulated protein kinase; P38, P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; CREB, c-AMP response element binding protein; -P, phosphorylation; CRE, cAMP response element; NR, nuclear receptor; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; Hsp90, heat shock protein 90; ARNT, aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator; XRE-NR, xenobiotic response element-nuclear receptor; XRE-AhR, xenobiotic response element-aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Created with BioRender.com.