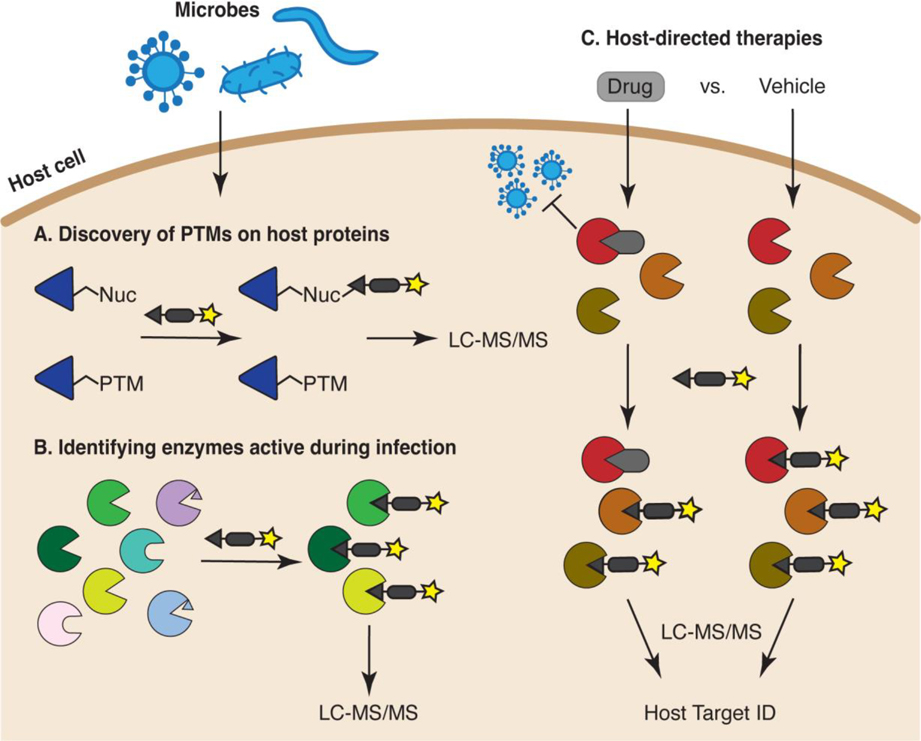
Figure 2:
Applications of ABPP for interrogating host biology during infection. (A) ABPP can be used to discover post-translationally modified sites within the proteome of infected cells. (B) ABPP can identify host enzymes that are active during infection. Enzymes containing active-site PTMs or autoinhibitory propeptides (represented as small triangles within the active site), or lacking a probe-reactive nucleophile (represented as enzymes with rounded active sites) will not be captured. (C) Competitive ABPP can uncover host enzymes targeted by anti-infective agents. For example, the proteomes of virus-infected cells treated with an antiviral drug (gray rounded rectangle) or vehicle control can be labeled with an activity-based probe. Enzymes that exhibit decreased probe-based enrichment in the presence of drug versus vehicle represent potential drug targets (red enzyme).