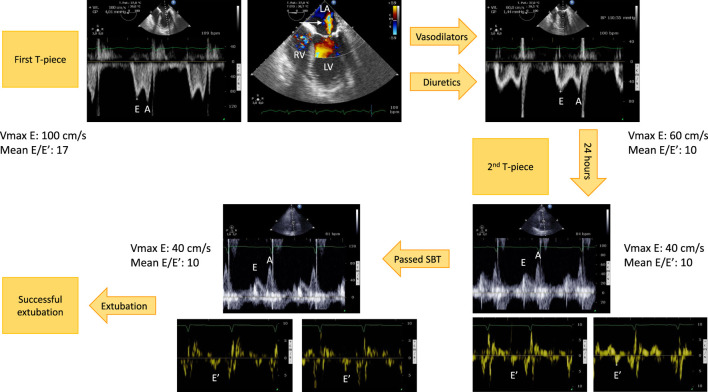
FIGURE 2.
Example of hemodynamic monitoring using echocardiography in a patient with left ventricular systolic dysfunction secondary to an ischemic heart disease who developed a weaning-induced pulmonary edema during the first T-piece trial which induced high blood pressure. Immediately after having reconnected the patient to the ventilator, a transesophageal echocardiography was performed. Mitral Doppler depicted elevated E wave velocity and mean E/E′ ratio, consistent with increased left ventricular filling pressure (upper left panel). There was only a mild functional mitral regurgitation (upper middle panel, arrow). Treatment associated short half-life sedative, ACE inhibitors and diuretics. With normalization of blood pressure and fluid removal, the mitral Doppler profile remained unchanged (E/A ratio ≈1), but velocities significantly decreased as well as mean E/E′ ratio (upper right panel). This allowed to perform a second T-piece trial 24 h later. Immediately before the procedure, mitral E wave velocity remained low, E/A ratio was <1, and mean E/E′ remained stable, denoting the absence of new rise in left ventricular filling pressure (3 lower right panels). The second spontaneous breathing trial was clinically successful. Echocardiography at the end of the 30-min T-piece trial depicted similar mitral Doppler velocity values, hence left ventricular filling pressure (3 lower left panels). The patient was then extubated successfully without any change of ongoing treatment. Abbreviations: LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RV, right ventricle.