Figure 2: Downregulation of M1BP activates JNK signaling in the developing eye.
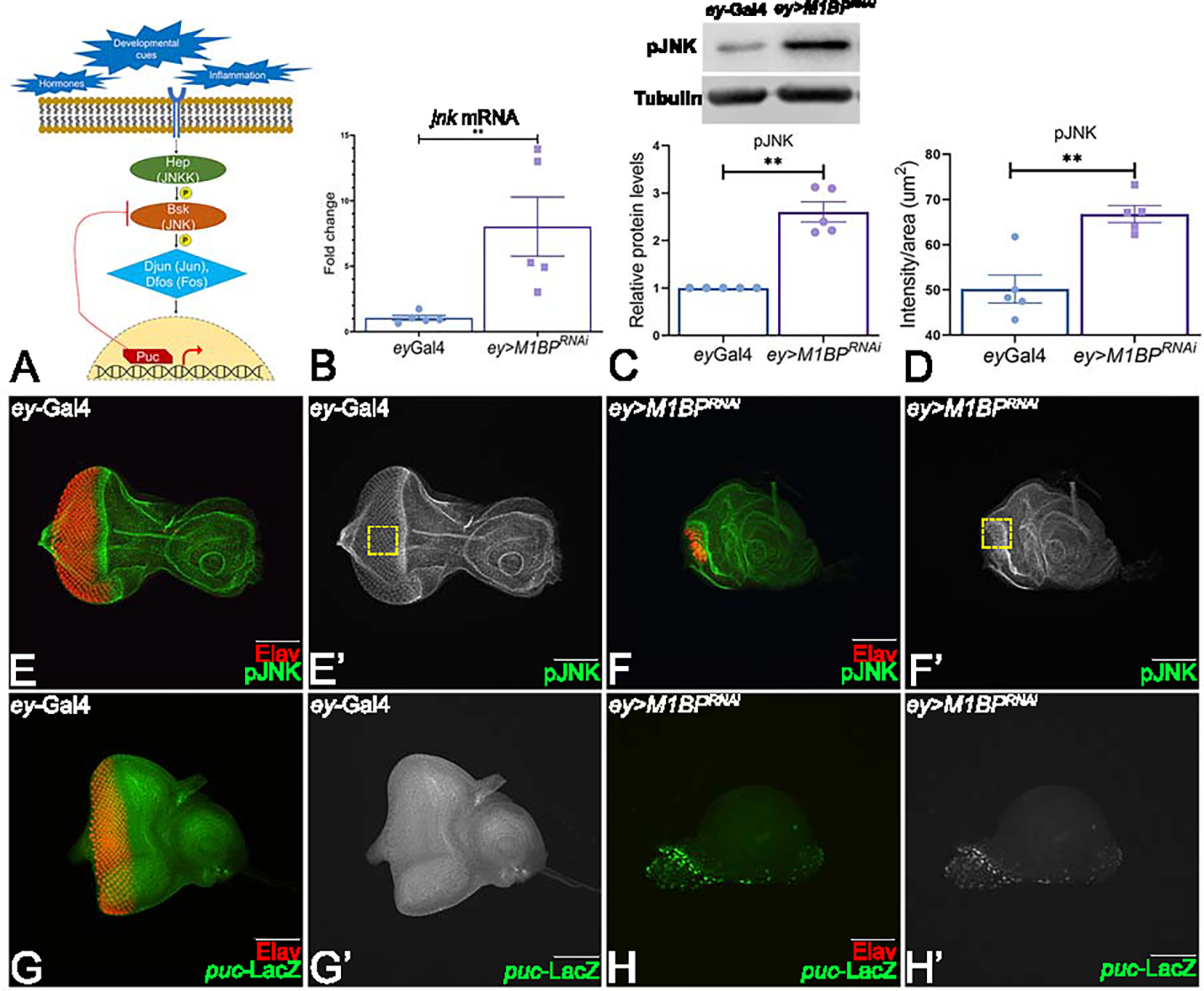
(A) Schematic representation of c-Jun NH (2)-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway. (B) Relative expression of jnk at the transcriptional level using quantitative real time PCR (qRT-PCR) in ey>M1BPRNAi and ey-Gal4 control eye-antennal imaginal discs. (C) Levels of phospho-JNK (pJNK) in a semi-quantitative Western Blot shows higher levels of JNK signaling in ey>M1BPRNAi compared to ey-Gal4 control. The tubulin bands serve as control for normalization. The quantification of p-JNK band intensity reveals a significantly higher levels in ey>M1BPRNAi background as compared to the control ey-Gal4. (D) Quantification of pJNK intensity using Fiji/ImageJ software (NIH). (E-H) Eye antennal imaginal disc of third instar larvae stained for pan-neuronal marker Elav (red) and (E, F) pJNK (green) and (G, H) puc-lacZ (green). Eye antennal imaginal disc showing split channel for (E’, F’) pJNK staining, (G’, H’) lacZ staining for (E, E’, G, G’) ey-Gal4 and (F, F’, H, H’) ey>M1BPRNAi. Graphs were plotted with mean +/− SEM. Statistical significance in each graph is shown by p-value: ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001; **p<0.01; *p<0.05. The orientation of all imaginal discs is identical with posterior to the left and dorsal up. The magnification of all eye-antennal imaginal disc is 20X unless specified.
