Figure 1.
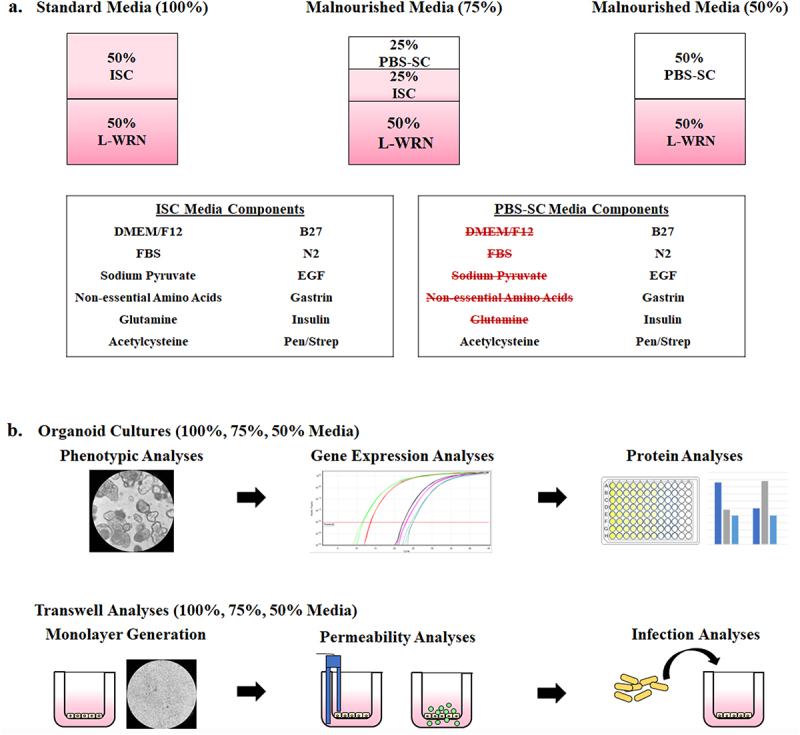
Malnourished media composition and study design. To generate malnourished organoids, certain media additives were eliminated to reduce nutritional content while maintaining cellular viability. Following establishment of media formulations to reduce protein, amino acid, and carbohydrate concentrations, both organoids and organoid-derived monolayers were incubated in the various media compositions and subsequently analyzed for the effects of malnourishment.
a. Malnourished media. The 50% L-WRN was essential to cellular viability and could not be removed or diluted. However, certain components of the ISC media could be removed without detrimental effects to cellular viability, and the volume was replaced with 1X PBS to generate 50% PBS-SC media. The standard media formulation (100%) is composed to 50% ISC media and 50% L-WRN media. The 75% malnourished media is composed of 25% PBS-SC, 25% ISC, and 50% L-WRN. The 50% media formulation is composed of 50% PBS-SC and 50% L-WRN. Overall, by diluting the ISC media, the concentration of protein, amino acids, and carbohydrates was reduced. All media types (100%, 75%, and 50%) also contained the inhibitors Y-27632 and A 83-01 in the L-WRN portion of the media.
b. Malnourished organoid and organoid-derived monolayer analyses.
Top: Organoids from three separate donors were cultured in the three different media formulations for seven days. The organoids were then analyzed for changes in phenotypic appearance, gene expression via qRT-PCR, and protein expression via immunofluorescence analysis and lactate dehydrogenase release, intestinal alkaline phosphatase secretion, and interleukin-8 secretion assays.
Bottom: The media formulations were also used to culture malnourished organoid-derived monolayers (mHIODEM). Following organoid generation in 100% media for seven days, organoids from the three separate donors were trypsinized, the cells were seeded onto transwells, and the monolayers were cultured for 13 days in the three different media formulations. The monolayers were differentiated with DAPT for the last 2 days of culturing (starting on day 11). Afterwards, the monolayers were analyzed for permeability via TEER and FITC-dextran passage, as well as susceptibility to infection via S. flexneri invasion analyses.
