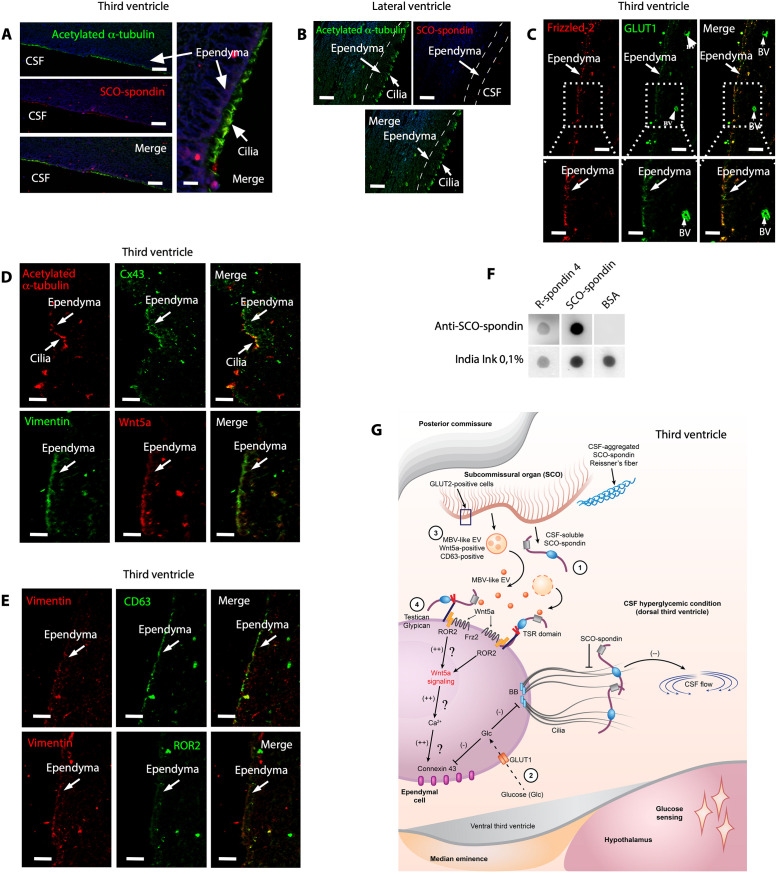
Fig 10. Human ependymal cells express Wnt5a, Frizzled-2, GLUT1, and Cx43 with SCO-spondin–like protein detected in the cilia.
(A and B) Immunohistochemical staining of SCO-spondin (red) and acetylated α-tubulin (green) in ependymal cells from the adult human brain. Scale bar: 15 μm. (C) Immunohistochemical staining of Frizzled-2 and GLUT1 in human ependymal cells. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D) Immunohistochemical staining of acetylated α-tubulin/Cx43 and vimentin/Wnt5a in human ependymal cells. Scale bar: 20 μm. (E) Immunohistochemical staining of vimentin/CD63 and vimentin/ROR2 in human ependymal cells. Scale bar: 20 μm. (F) Dot-blot analysis with anti-SCO-spondin. The samples were SCO-spondin and R-spondin-4. (G) Overview of hyperglycemic conditions in the third ventricle, SCO cell activation, and the effect of SCO-spondin and Wnt5a on ependymal cells. Similar to β-pancreatic cells, SCO cells express GLUT2, a low-affinity glucose transporter. Under hyperglycemic conditions, the increase in the intracellular glucose concentration is expected to raise the ATP content, stimulating the secretion of SCO-spondin into the CSF (number 1). In ependymal cells, the increase in the glucose concentration changes ciliary beating (number 2). Additionally, it may reduce Cx43-mediated functional coupling. SCO-spondin (soluble in CSF) preferentially binds to the apex of dorsal ependymal cells, further preventing normal ciliary beating. CSF flow shows a transient decline, promoting glucose sensing in the basal hypothalamus (bottom pink area). When the glucose level in the CSF is high, SCO cells also release Wnt5a, possibly via CD63-positive MVB-like EVs (number 3). Wnt5a bound to ROR2 (very likely anchored to testican or glypican) can be internalized (number 4) [38,40] and probably activating the noncanonical β-catenin signaling pathway (number 4) [36]. CX43 is uncoupled under hyperglycemic conditions, and this alteration may be reversed when the intracellular calcium increases [36]. The original blot for this figure (F) can be found in S1 Raw Images. BV, blood vessel; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; Cx43, connexin-43; EV, extracellular vesicle; MVB, multivesicular body; ROR2, Frizzled 2/receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor-2; SCO, subcommissural organ.