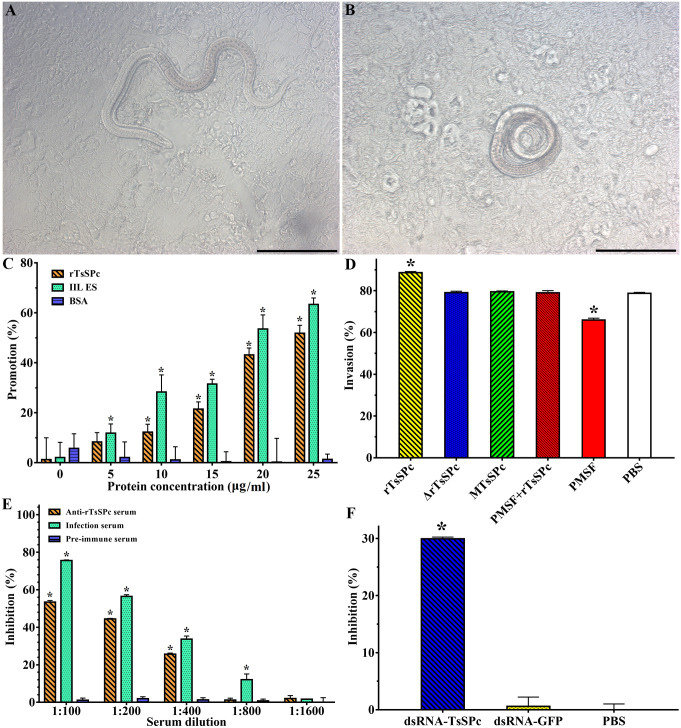
Fig 16. rTsSPc promoted larval invasion and anti-rTsSPc serum and dsRNA inhibited the invasion.
The ML was first activated to IIL larvae using 5% swine bile at 37 °C for 2 h, and then added to the Caco-2 cell monolayer. After co-cultivation for 2 h, larval invasion was observed under a microscopy. A: invaded larvae in the monolayer were active, and the cell monolayer integrity was disrupted. B: non-invaded larvae were spirally coiled on the surface of the cell monolayer. C: facilitation of rTsSPc on larval invasion. D: heat-inactivated rTsSPc, MTsSPc and PMSF-treated rTsSPc had no any facilitation on the invasion. E: inhibition of anti-rTsSPc antibodies on larval invasion. F: TsSPc-specific dsRNA suppressed larval invasion. The data were normalized to the PBS group and represented the mean ± SD of three independent tests. Δ rTsSPc represents the heat-inactivated rTsSPc. *P < 0.01 compared to the BSA, PBS or pre-immune serum group. Scale bars: 200 μm.