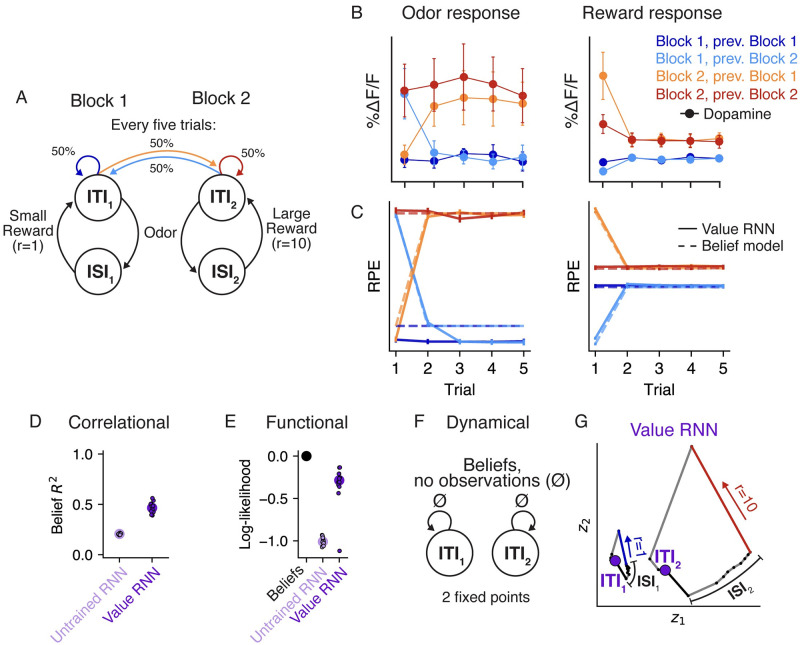
Fig 7. Value RNNs trained on Babayan et al. (2018) [10] reproduce Belief RPEs and learn belief-like representations.
A. Task environment of Babayan et al. (2018) [10]. Each trial consists of an odor and a subsequent reward. The reward amount depends on the block identity, which is resampled uniformly every five trials. B. Average phasic dopamine activity in the VTA of mice trained on the task at the time of odor (left) and reward (right) delivery. Activity is shown separately as a function of the trial index within the block (x-axis) and the current/previous block identity (colors). Reproduced from Babayan et al. (2018) [10]. C. Average RPEs of the Belief model (dashed lines) and an example Value RNN (solid lines). Same conventions as panel B. D. Total variance of beliefs explained (R2) using a linear transformation of model activity. Same conventions as Fig 4B. E. Cross-validated log-likelihood of linear decoders trained to estimate true states using RNN activity. Same conventions as Fig 4C. F. Dynamics of beliefs in the absence of observations. Same conventions as Fig 5A. G. Trajectories of an example Value RNN’s activity, in the 2D subspace identified using PCA, during an example trial from Block 1 (left) and Block 2 (right). These two dimensions explained 68% of the total variance in the Value RNN’s activity across trials. Putative ITI states indicated as purple circles. Same conventions as Fig 5B.