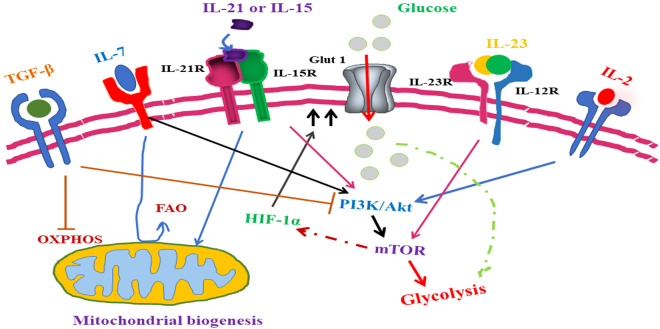
Figure 5.
Role of cytokine-mediated signaling in T-cell lymphoma metabolic reprogramming. TGF-β, an anti-inflammatory cytokine, inhibits T lymphoma cell glycolysis whereas IL-7 signaling promotes glycolysis through upregulation of Glut1 expression. With a similar role in antioxidant production, IL-15- and IL-21-mediated signaling plays an important role in oxidative phosphorylation along with mitochondrial biogenesis inside the T-lymphoma cells. IL-15- and IL-21-mediated signaling induces the mTOR pathway and subsequent alternation of T-lymphoma cell metabolism. In addition to promoting the growth of Th17 helper cells, IL-1β also induces the mTOR pathway. Although IL-2 promotes mTOR activity in both CD4+T cell and CD8+ T cell through different pathways, in CD8+ T cell, IL-2 induces mTOR through PDK whereas in CD4+ T cell, IL-2 induces mTOR through activation of the PI3/Akt pathway. Upregulation in amino acid intake by T-cell lymphoma cells is promoted through overexpression of SLC7A5.