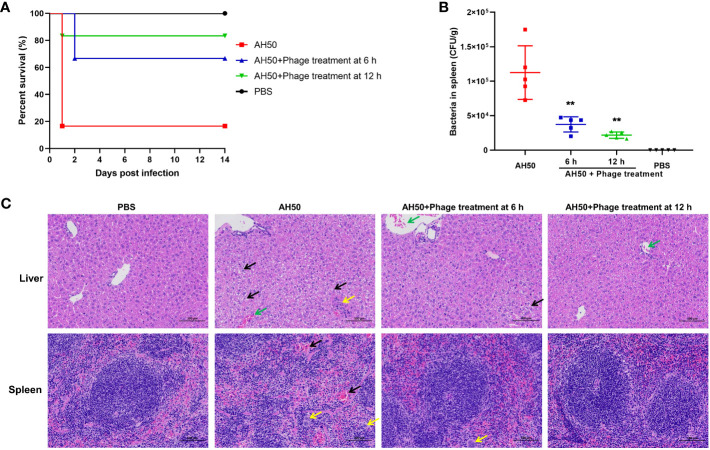
Figure 7.
The therapeutic effect of phage PEC9 against APEC infection in vivo. (A) Survival rates of mice. The mice were administered intraperitoneally with phage PEC9 at 6 or 12 h post-infection. Mice injected with APEC AH50 or PBS only were used as the control groups. The survival rates of mice were monitored. (B) Bacteria concentrations in spleens of the phage-administered and control mice. The live mice were sacrificed at 24 h post-infection. (** P < 0.01). (C) Histopathological examination of mouse livers and spleens in 24 h after infection. From left to right, the pathological section results of livers and spleens of mice in the healthy group, the infection control group, the 6 h treatment group, and the 12 h treatment group. In the liver pathological micrographs, the black arrows indicate moderate watery degeneration of diffuse liver cells, swelling of liver cells, loose cytoplasm, and small vacuoles in the cytoplasm. The yellow arrow indicates necrotic foci in lobules, broken nuclei of hepatocytes, disintegration of cytoplasm, and minimal granulocyte infiltration. The green arrows indicate central vein congestion. In the spleen pathological micrographs, the black arrows indicate that the number of lymphocytes is reduced and the red pulp is moderately congested. The yellow arrows indicate that multinucleated giant cell increase.