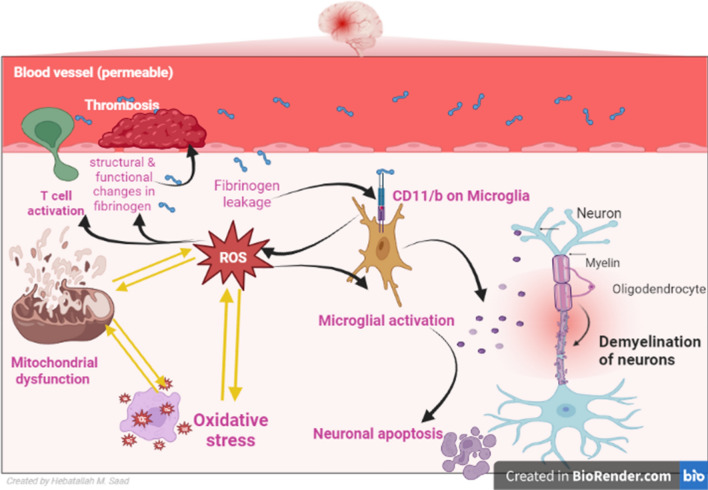
Fig. 4.
Oxidative stress/mitochondrial dysfunction/fibrinogen in multiple sclerosis (MS): fibrinogen binds the CD11b receptor in microglia leading to the activation of NADPH oxidase and the release of Reactive oxygen species (ROS) leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and injury of oligodendrocytes. Additionally, oxidative stress induces structural and functional changes in fibrinogen leading to thrombosis. ROS trigger peripheral activation of T cells and the development of autoreactive T cells. ROS triggers the activation of microglia and induction of neuronal apoptosis