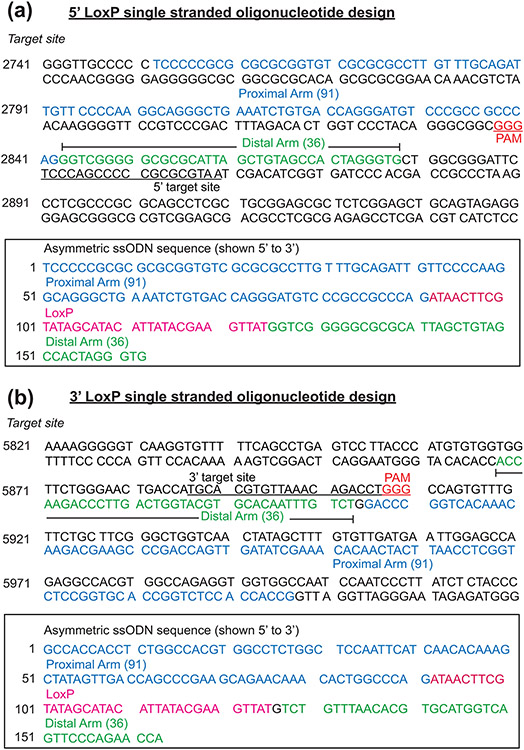
FIGURE 2.
The design and position of the 5’ and 3’ ssODNs that were used to create the mouse Egr1 floxed allele. (a) Shown is the sequence of the 5’ target site in intron 1 of the mouse Egr1 allele. Sequences in blue (91 base pairs (bp)) and green (36 bp) represent the asymmetric homology arms that are proximal and distal respectively relative to the location of the 3’ protospacer adjacent motif (PAM (red)); the ssODN sequence is complementary to the non-targeted strand. The sequence of the 5’ target site is underlined whereas the 3’ PAM (GGG) site is highlighted in red. The box contains the sequence (in the 5’ to 3’ direction) of the ssODNs that were used for CRISPR/Cas9 mediated homology directed repair. The LoxP sequence is highlighted in red, the underlined sequence shows the target sequence disrupted by the LoxP sequence in the ssODN donor. The proximal and distal homology arm sequences are highlighted in blue and green respectively. (b) The sequence of the 3’ LoxP target site located 3’ to the mouse Egr1 gene. The sequences of the proximal and distal asymmetric homology arms are displayed blue and green respectively. The location and sequence of the 3’ target site is underlined with the 3’ PAM shown in red (GGG). The box encloses the sequence of the ssODN donor that was used to insert the LoxP site in the 3’ location relative to the mouse Egr1 gene. The underlined target sequence is disrupted by the LoxP sequence (highlighted in red), which is flanked by the proximal and distal homology arms that are highlighted in blue and green respectively.