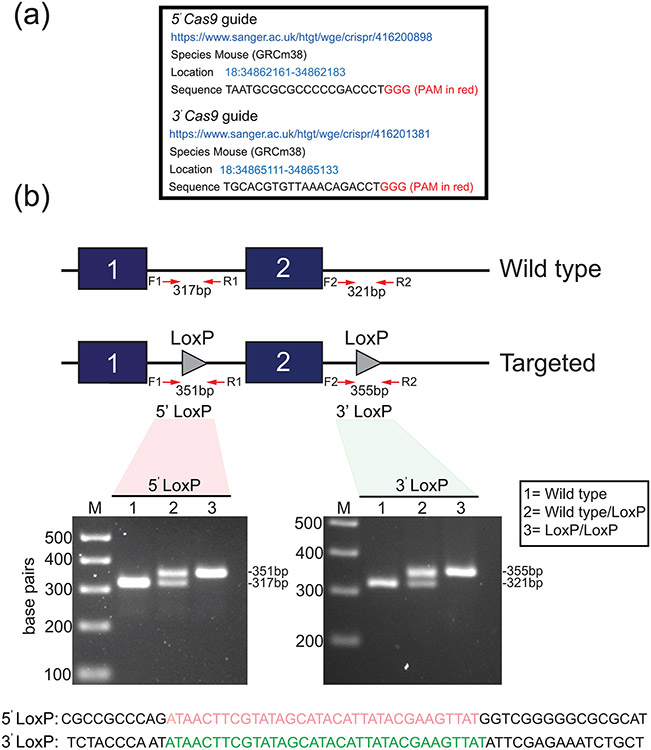
FIGURE 3.
Generation of the murine Egr1 floxed allele. (a) The location information of the 5’ and 3’ Cas9 guide sequences (sense strand) that were used to generate the murine Egr1 floxed allele by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing is shown. Note: in vitro transcribed sgRNAs were microinjected into C57BL/6NJ zygotes. (b) Schematic of the CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeting strategy to insert the LoxP sites (grey triangles) into intron 1 of and 3’ from the Egr1 gene to flox exon 2. The location of the forward and reverse PCR primers to amplify the 5’ and 3’ LoxP sites is indicated. Using forward and reverse PCR primers (F1 and R1 primers to amplify the 5’ LoxP site (351 bp); F2 and R2 primers to amplify the 3’ LoxP site (355 bp)), the gel shows a typical genotype result for wild type (lane 1 (no LoxP sites (317/321 bp)), wild type/LoxP (lane 2 (heterozygote (Egr1f/+ (317/321 and 351/355 bp)), and LoxP/LoxP (lane 3 (homozygous (Egr1f/f) for the 5’ and 3’ LoxP insertion (351/355 bp). The PCR genotyping result shown was performed on tail biopsy genomic DNA from F2 generation mice. The sequences for the 5’ (red) and 3’ (green) LoxP sites that were carried by these mice are shown.