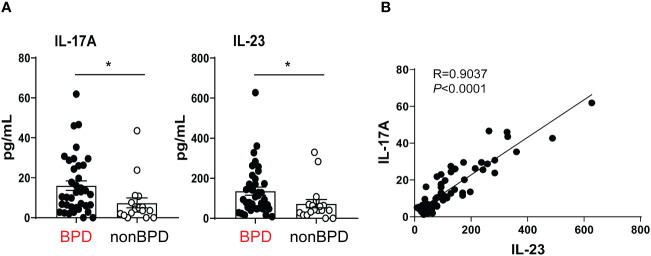
Figure 1.
Inflammatory cytokines IL-17A and IL-23 are elevated in the tracheal aspirates of premature infants who later develop BPD. Mechanically ventilated premature infants without other comorbidities were recruited to the study. Tracheal aspirates were collected during the first week of life. (A) IL-17A and IL-23 protein levels were detected by Multiplex ELISA in the supernatants of the tracheal aspirates. BPD diagnosis was recorded based on chart review once the subjects reached 36 weeks postmenstrual age. Because death is a competing outcome for BPD, infants who died before 36 weeks postmonstrual age were included in the BPD/death group. This group included 37 infants. 17 infants did not develop BPD (No BPD). Both IL-17A and IL23 protein levels were elevated in infants who later developed BPD compared to infants who did not go on to develop BPD. *p<0.05 (unpaired t-test). (B) IL-23 protein levels significantly correlated with IL-17A levels. Pearson’s correlation analysis. R=0.9037, p<0.0001.