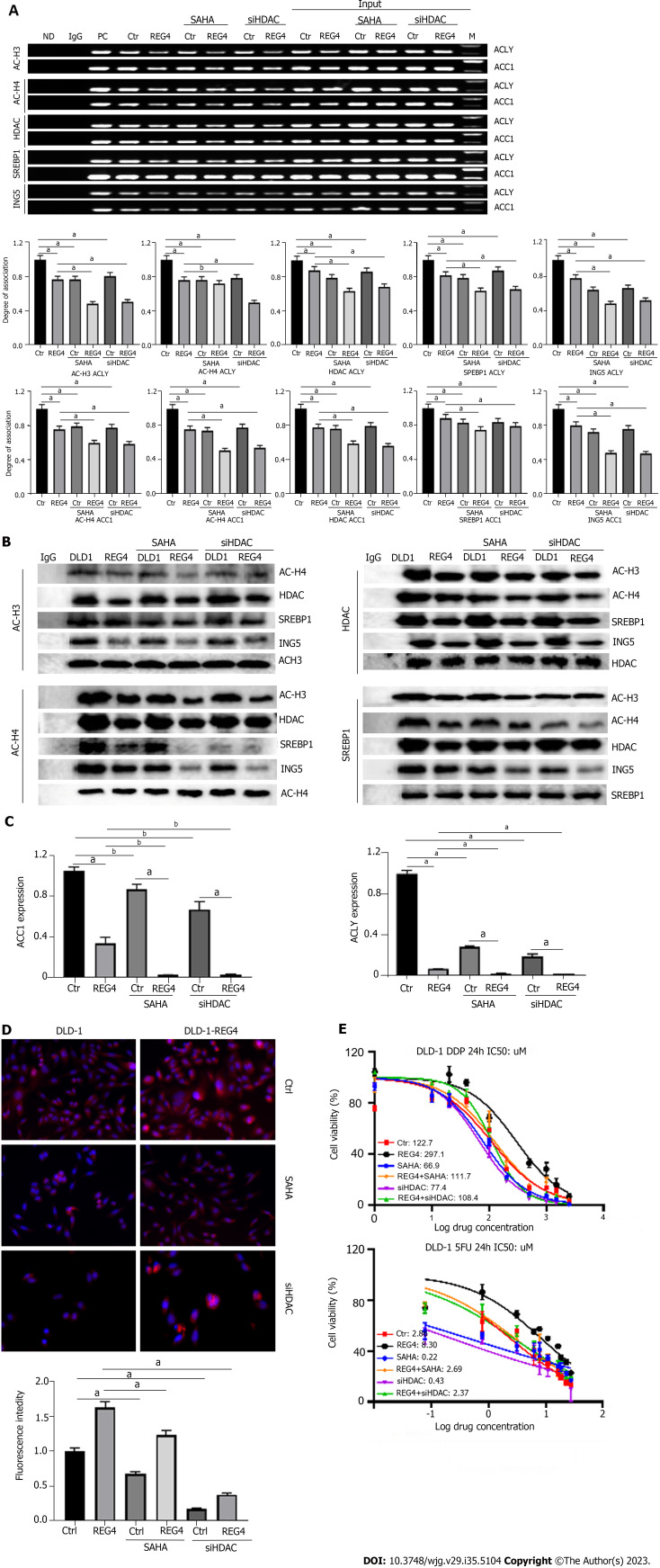
Figure 3.
Full-length regenerating gene 4 weakened the transcription of acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 and ATP-citrate lyase. A: DLD-1 cells and full-length-regenerating gene 4 (FL-REG4) transfectants were treated with suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) or small interfering RNA against histone deacetylase (siHDAC), and analyzed by chromatin immunoprecipitation; B: DLD-1 cells and FL-REG4 transfectants were treated with SAHA, or siHDAC, and analyzed by co-immunoprecipitation assay using anti-anti-acetyl (AC)-acetyl-histone 3-AC-histone 4, anti-HDAC, anti-sterol-regulatory element binding protein 1 or anti-inhibitor of growth protein 5 antibody; C: DLD-1 cells and FL-REG4 transfectants were treated with SAHA or siHDAC, and analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; D: DLD-1 cells and FL-REG4 transfectants were treated with SAHA or siHDAC, and analyzed by Nile red staining; E: DLD-1 cells and FL-REG4 transfectants were treated with SAHA or siHDAC, and analyzed by half maximal inhibitory concentration assay of 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin. aP < 0.001; bP < 0.01. REG4: Regenerating gene 4; SAHA: Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid; siHDAC: Small interfering RNA against histone deacetylase; IgG: Immunoglobulin G; ND: No DNA; ACC1: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1; ACCY: ATP-citrate lyase; AC-H3: Acetyl-acetyl-histone 3; H4: Histone 4; SREBP1: Sterol-regulatory element binding protein 1; ING5: Inhibitor of growth protein 5; Ctr: Control DLD-1 cells; PC: Positive control.