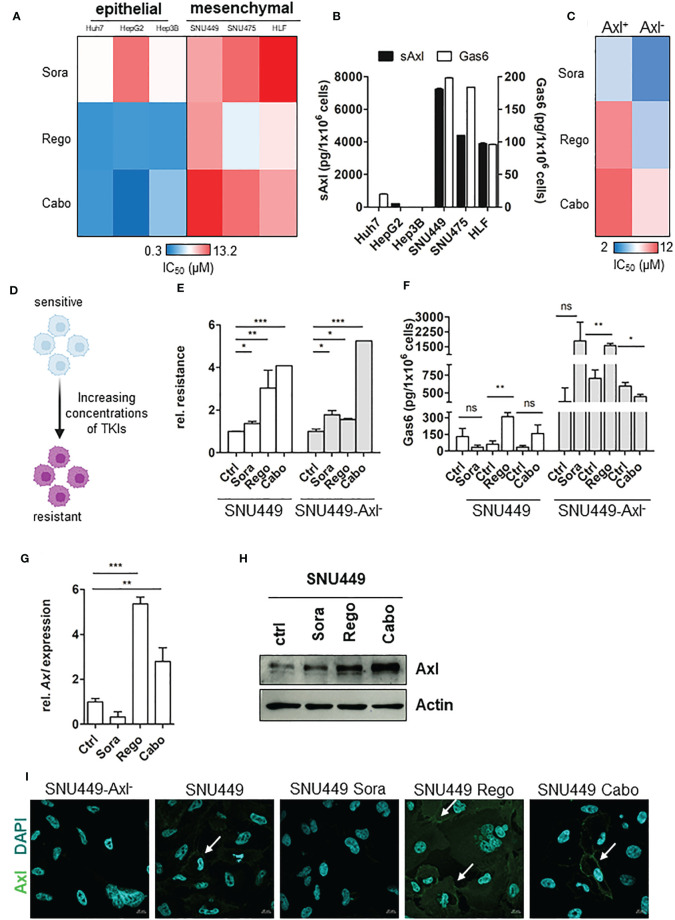
Figure 1.
Axl modulates cellular response to TKIs. (A) Heat map of IC50 values showing sensitivities of HCC cells against TKIs. (B) Release of sAxl and Gas6 into supernatants of HCC cells as determined by ELISA. (C) Heat map of IC50 values indicating sensitivities of parental and Axl-deficient HCC cells against TKIs. (D) Model depicting the generation of TKI-resistant cells. (E) Relative response of parental (ctrl, control, naïve) and resistant HCC cells against TKIs in Axl-proficient and Axl-deficient background. IC50 values were calculated and normalized to sensitive control. Sensitivity of the control was set to the value of 1. (F) Release of Gas6 into supernatants of control (naïve) and TKI-resistant cells as determined by ELISA. (G, H) Transcript and protein levels of Axl in control (naïve) and TKI-resistant HCC cells as analyzed by qPCR (G) and Western Blotting (H), respectively. (I) Expression of Axl (green) in control (naïve) and Sora-, Rego- and Cabo-resistant HCC cells as examined by immunofluorescence microscopy. Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). White arrows show Axl expression on cell membranes. Data are expressed as mean +/- SD. ns: p > 0.05; *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001. TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; Sora, Sorafenib; Rego, Regorafenib; Cabo, Cabozantinib; sAxl, soluble Axl.