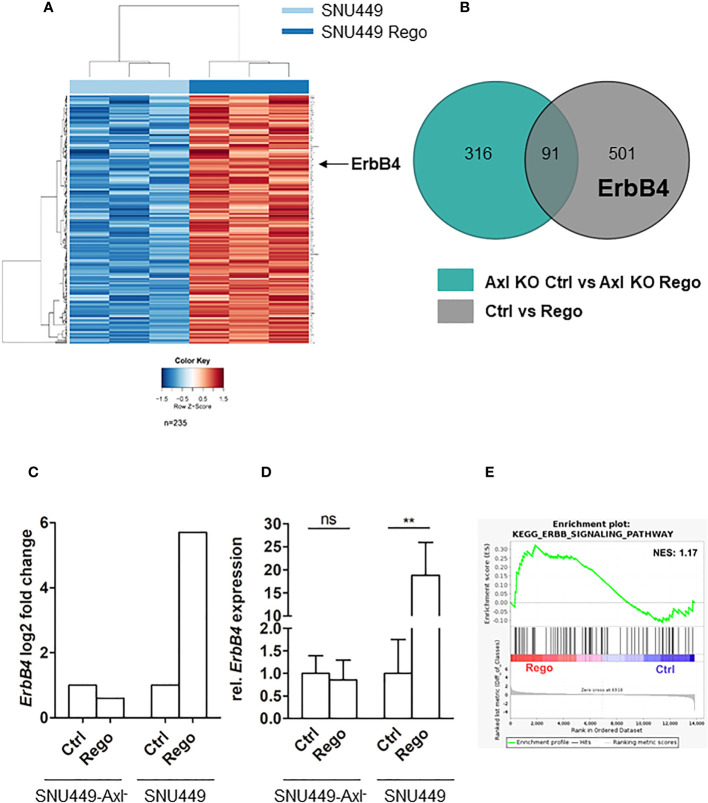
Figure 2.
Axl expression associates with induction of ErbB4 levels in Rego-resistant HCC cells. (A) Heat map of differentially expressed transcripts in control (naïve; light blue bar) vs. Rego-resistant SNU449 cells (dark blue bar). Heat map colors range from blue to red for low to high relative expression (see color gradient at bottom). Arrow indicates the row showing ErbB4 expression in Rego-resistant HCC cells. (B) Axl-dependent genes associating with Rego resistance were identified by overlapping differentially expressed genes of control vs Rego-resistant cell comparisons in an Axl-deficient (green) or Axl-proficient (grey) background. (C) Log2FC of ErbB4 expression in Rego-resistant versus control cells based on RNA-Seq data. (D) Relative mRNA expression of ErbB4 in control and Rego-resistant SNU449 and SNU449-Axl- as determined by qPCR. Data are expressed as mean +/- SD. (E) GSEA shows enrichment of ErbB signaling in Rego-resistant SNU449 cells. ns: p > 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01. GSEA, Geneset enrichment analysis; Rego, Regorafenib; FC, fold change.