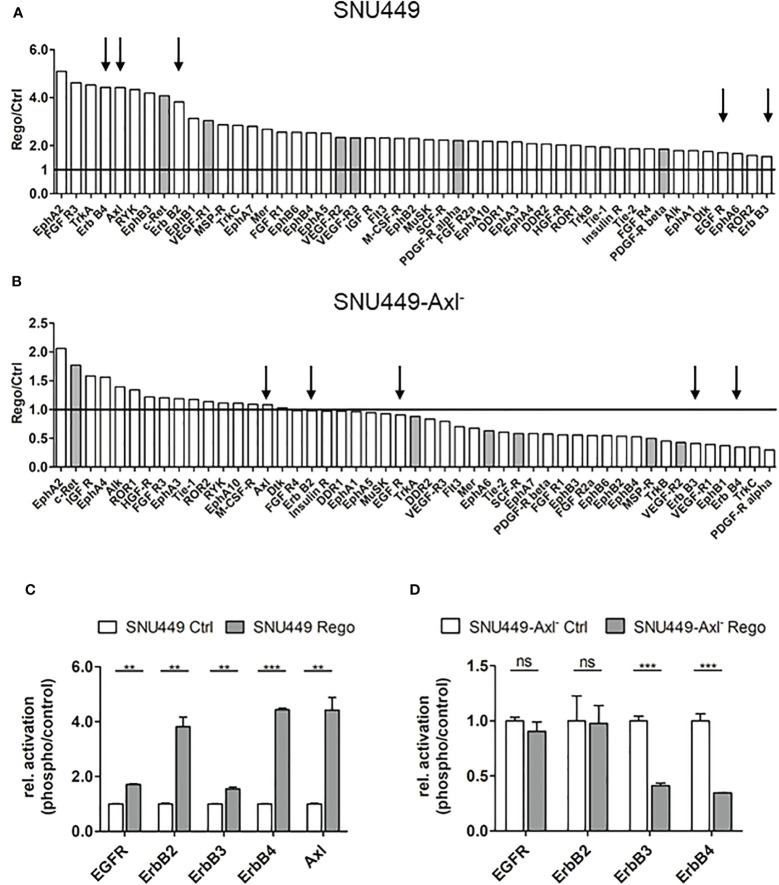
Figure 3.
Axl-dependent activation of ErbB receptors in Rego-resistant HCC cells. (A, B) Quantification of phospho-RTK signals comparing control (ctrl, naïve) and Rego-resistant SNU449 cells in the Axl-proficient (A) and Axl-deficient background (B). Signal intensities of phospho-RTKs were normalized to intensities of controls. Grey bars depict targets of Regorafenib. Arrows indicate Axl and members of the ErbB receptor family and black lines indicate unchanged phosphorylation levels (A, B). (C, D) Relative abundance of selected phospho-RTKs in control (naïve) vs. Rego-resistant SNU449 cells in the Axl-positive (C) and Axl-negative background (D). Data are expressed as mean +/- SD. ns: p > 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001. RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; Rego, Regorafenib.