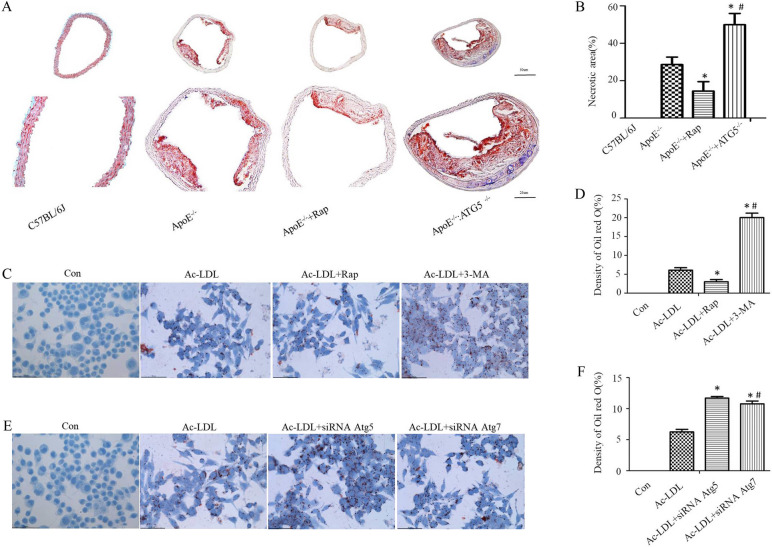
Fig. 2.
Autophagy attenuates the area of necrotic core in plaques and inhibits the formation of foam cells. ApoE−/−, ApoE−/− + Rap and ApoE−/−: ATG5−/− mice were fed for 16 weeks with western diet (n = 10) to trigger atherosclerosis. A Lipids in the aortic root were stained with oil red O. B Assessment of the necrotic area quantitatively. Data are expressed as mean ± SE (One way ANOVA showed that there was statistical significance among groups. *P < 0.05 vs. ApoE−/− mice [n = 10]; #P < 0.05 vs. ApoE−/− + Rap on a western diet [n = 10]; Student’s t-test showed that there was statistical significance between ApoE−/− + Rap and ApoE−/− mice, P < 0.01; in addition, there was statistical significance between ApoE−/−: ATG5−/− mice and ApoE−/− mice, P < 0.01). C–E Autophagy inhibited the conversion of macrophages into foam cells. The cells were activated by 50-μg/mL Ac-LDL in the presence of rapamycin, 3-MA, siRNA Atg5 and siRNA Atg7 for 30 h and subsequently stained with oil red O. D, F Quantitative analysis of the intensity of oil red O staining. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (One way ANOVA showed that there was statistical significance among groups. *P < 0.05 vs. the Ac-LDL group; #P < 0.05 vs. the Ac-LDL + Rap and Ac-LDL + siRNA Atg5 groups [n = 6 independent experiments])