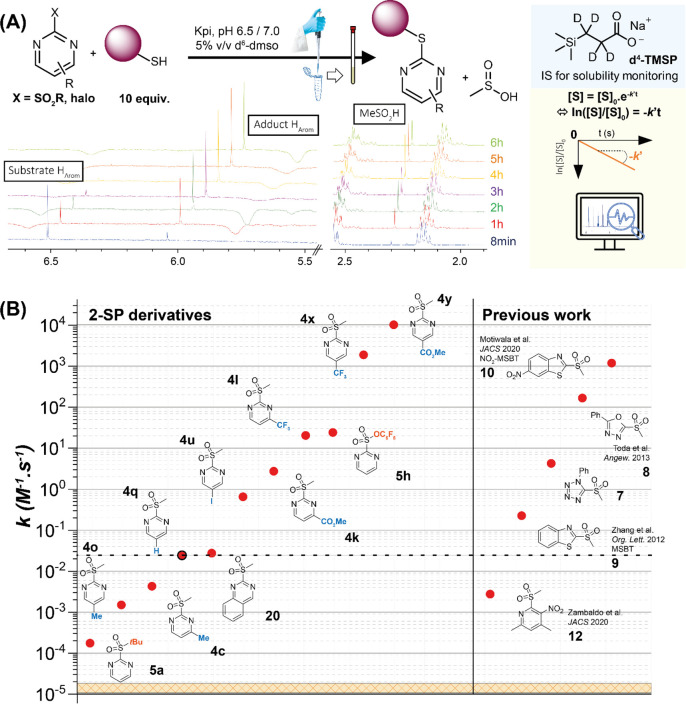
Figure 3.
In vitro determination of electrophilic reactivity of compounds. (A) NMR assay setup for warhead/GSH reaction rate constant determination and chemoselectivity monitoring, over a 6 h time scale. Purple bead = GSH. Hydrolytic stability was determined in the same way over 36 h. d4-Trimethylsilylpropanoate (TMSP, blue box) was used as an internal standard for monitoring the warhead solubility. Second-order reaction rate constants (k) were obtained from their pseudo-first-order counterparts (k′), by time-dependent normalized integration of the disappearing warhead signals. An example NMR stack for the representative reaction of 4,6-dimethoxy-2-methylsulfonylpyrimidine with GSH shows time-dependent signal evolution toward quantitative formation of arylated GSH and generation of methanesulfinic acid (2.3 ppm). (B) Experimental second-order rate constants (y axis, log10 scale) for the reaction of representative 2-SP derivatives (left, 11 out of ca. 40 examples) and previously reported heteroarylsulfones (right) with GSH in a KPi buffer, pH 7.0, 20 °C. All rate constants were calculated as an average of at least two independent measurements. Numerical values and standard deviations at both pH 7.0 and 6.5, along with a full list of 2-SPs and other electrophile types tested, are presented in Tables S2–S6 and Figure S4. The horizontal dashed line marks the reaction rate of 2-methylsulfonylpyrimidine at pH 7.0, as a reference when comparing with other reagents (see main text).