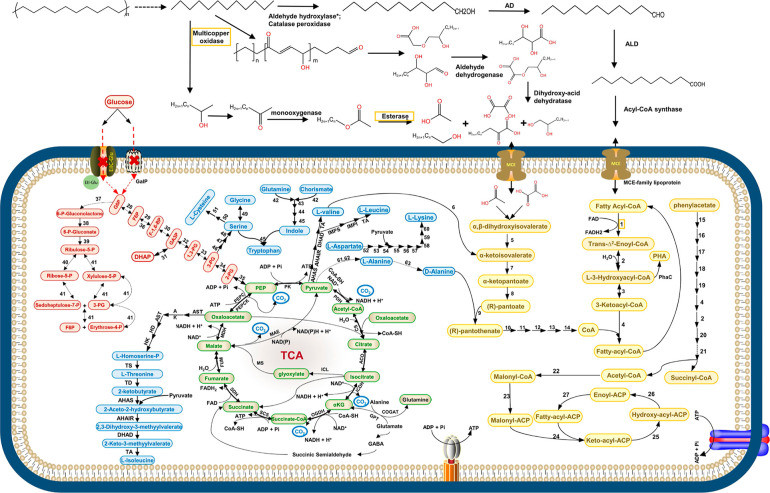
Figure 5.
Conceptual model of metabolic pathways of A34 when grown in defined medium with PE as the carbon source. The pathways are illustrated based on the proteomics data, FTIR, and GC–MS data. Solid arrow represents one-step reaction; broken-line arrow represents the absence of the corresponding enzyme in proteomics data or unknown enzymes. The initial PE depolymerization step indicated by a broken-line arrow might involve multiple enzymes, such as multicopper oxidase, catalase peroxidase, esterase, lipase, and others. PE functional group changes were observed after incubation with crude enzymes of combination of a multicopper oxidase peg 1726 and an esterase peg 6607 (Figure S7). The orange frame highlighted the two types of extracellular key PE degradation enzymes. Color key for intracellular pathways: light brown, fatty acid β-oxidation; fatty acid biosynthesis, phenylacetate metabolism, biosynthesis of pantothenate, and CoA; light green, TCA cycle and the associated pyruvate cycle, glyoxylate cycle, and GABA skanehunt; light red, glycolysis, glycogenolysis, and pentose phosphate pathway; and light blue, biosynthesis of amino acids and secondary metabolites. PE oxidation and depolymerization enzymes: alkane hydroxylase* (genes exist but protein not detected); AD, alcohol dehydrogenase; ALD, aldehyde dehydrogenase; enzymes in fatty acid β-oxidation: 1, acyl-CoA oxidase or acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; 2, enoyl-CoA dehydratase; 3, 3-hydroxyacyl-CoAcdehydrogenase; and 4, β-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase. Enzymes in biosynthesis of pantothenate and CoA: 5, dihydroxy-acid dehydratase; 6, valinepyruvate aminotransferase; 7, ketopantoate hydroxymethyltransferase; 8, ketopantoate reductase PanG or ketol-acid reductoisomerase [NADP(+)]; 9, pantothenate synthetase; 10, pantothenate kinase; 11, phosphopantothenoylcysteine synthetase; 12, phosphopantothenoylcysteine decarboxylase; 13, phosphopantetheine adenylyltransferase; and 14, dephospho-CoA kinase. Enzymes in phenylacetate metabolism: 15, phenylacetate-coenzyme A ligase; 16, 1,2-phenylacetyl-CoA epoxidase; 17, 1,2-epoxyphenylacetyl-CoA isomerase; 18, 2-oxepin-2(3H)-ylideneacetyl-CoA hydrolase; 19, 3-oxo-5,6-dehydrosuberyl-CoA semialdehyde dehydrogenase; 20, 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase; 21, 3-oxoadipyl-CoA those. Enzymes in fatty acid biosynthesis: 22, acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase; 23, malonyl CoA-ACP acyltransferase; 24, 3-oxoacyl-ACP synthase of FASI, KASI, or KASII; 25, 3-oxoacyl-ACP reductase; 26, β-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratase; and 27, enoyl-ACP reductase. Enzymes in PHA biosynthesis: PhaC, PHA synthase. Enzymes in the TCA cycle and associated pyruvate cycle, glyoxylate cycle, and GABA shunt: PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; CS, citrate synthase; ACO, aconitate hydratase; ICDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase; OGDH, 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase; SCS, succinyl coenzyme A synthetase; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase; FUM, fumarate hydratase; MDH, malate dehydrogenase; PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; PEPC, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase; PK, pyruvate kinase; MAE, NAD-dependent malic enzyme; ICL, isocitrate lyase; MS, malate synthase G; GOGAT, glutamate synthase; GDC, glutamate decarboxylase; GAT, GABA aminotransferase; and SSADH, succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase. Enzyme in glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and the pentose phosphate pathway: 28, glucose-6-phosphate isomerase; 29, 6-phosphofructokinase; 30, fructose-bisphosphate aldolase; 31, triosephosphate isomerase; 32, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate ketol-isomerase; 33, phosphoglycerate kinase; 34, phosphoglycerate mutase; 35, enolase; 36, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase; 37, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; 38, 6-phosphogluconolactonase; 39, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase; 40, ribose-5-phosphate isomerase; and 41, transketolase. Enzymes in biosynthesis of amino acids: l-threonine, l-isoleucine, l-valine, and leucine: AST, aspartate aminotransferase; AK, aspartate kinase; ASD, aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase; HD, homoserine dehydrogenase; HK, homoserine kinase; TS, threonine synthase; TD, threonine dehydratase; AHAS, acetolactate synthase; AHAIR, acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase; DHAD, dihydroxy-acid dehydratase; TA, branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase; IPMS, isopropylmalate synthase; IPMI, α-isopropylmalate isomerase; IPMD, α-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase; tryptophan: 42, anthranilate synthase; 43, anthranilate phosphoribosyltransferase; 44, phosphoribosylanthranilate isomerase 45, tryptophan synthase; l-serine, glycine, and l-cysteine: 46, d-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase; 47, phosphoserine aminotransferase, 48, phosphoserine phosphatase; 49, serine hydroxymethyltransferase; 50, serine acetyltransferase; 51, cysteine synthase; l-lysine: 52, aspartokinase; 53, aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase; 54, 4-hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate synthase; 55, 4-hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate reductase; 56, 2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine-2,6-dicarboxylate N-succinyltransferase; 57, N-succinyl-l,l-diaminopimelate aminotransferase; 58, N-succinyl-l,l-diaminopimelate desuccinylase; 59, diaminopimelate epimerase; 60, diaminopimelate decarboxylase; l-valine, 61, alanine dehydrogenase; 62, alanine transaminase; and 63, alanine racemase.