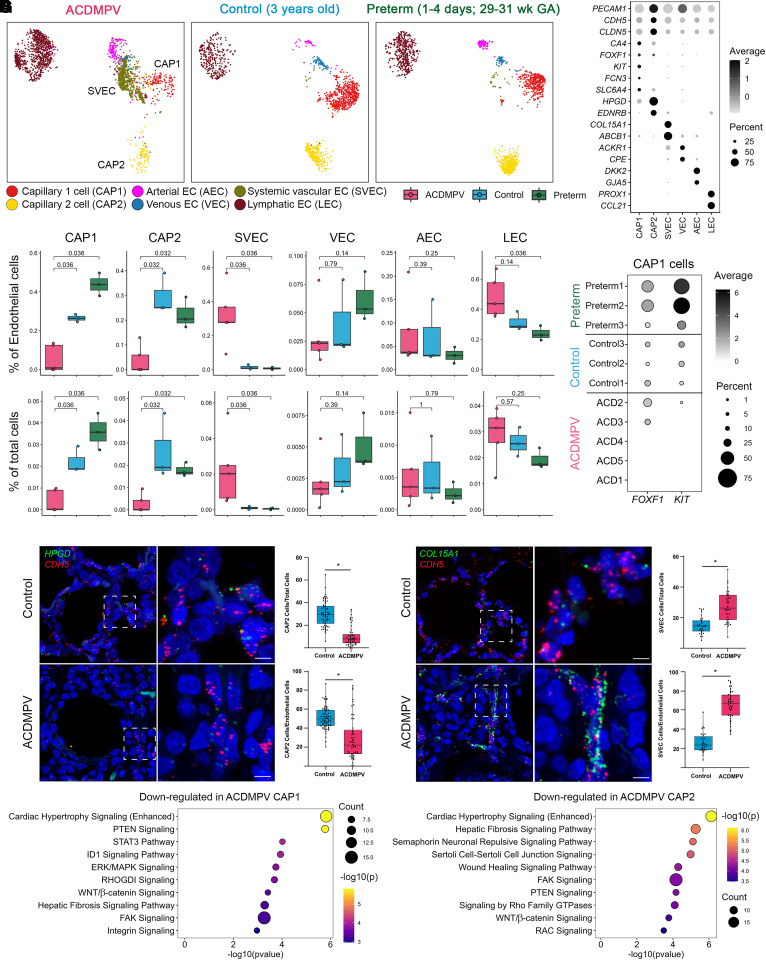
Figure 3.
Cell and gene expression changes in lung endothelial cells (ECs) in alveolar capillary dysplasia with misalignment of pulmonary veins (ACDMPV). (A) Uniform manifold approximation and projection embedding of ECs from snRNA-seq of ACDMPV (n = 5), control (n = 3; 3 yr old), and preterm neonate (n = 3; 1–4 d of age and 29–31 wk of GA) lungs. Cells are colored by the predicted EC types. (B) Dot plot of expression of marker genes for EC types. Gene expression with percentage ⩾5% is shown. (C) Changes in EC proportions in snRNA-seq of ACDMPV compared with control infant or preterm neonate lungs. P value represents the significance of the difference in cell proportions using a two-tailed Wilcoxon rank sum test. (D) Expression of FOXF1 and KIT RNA in capillary 1 (CAP1) cells of individual donors. Gene expression with percentage ⩾1% is shown. (E and F) RNAscope analysis validating the decrease in HPGD/cadherin 5 (CDH5) coexpressing capillary 2 (CAP2) cells in ACDMPV (n = 6) (ACD1 shown) versus control (n = 7) (1-day-old shown) lungs (E) and increase in COL15A1/CDH5 SVECs (F) in ACDMPV (n = 5) (ACD3 shown) versus control (n = 4) (13-month-old shown) lungs. Scale bars, 5 μm. (G) Ingenuity Pathway Analysis identified pathways significantly associated with genes downregulated in CAP1 (left) or in CAP2 (right) cells in snRNA-seq of ACDMPV versus control lungs. Shown are the top 10 signaling pathways ranked by P value. Downregulated genes satisfied the following criteria: differentially expressed in ACDMPV versus control snRNA cells (P < 0.05, fold change ⩾ 1.5, and expression percentage ⩾ 20%), selectively expressed in the selected cell type in either ACDMPV or control lung snRNA-seq data (P < 0.05, fold change ⩾ 1.2, and expression percentage ⩾ 10%), and not a mitochondrial gene. The two-tailed Wilcoxon rank sum test was used for differential expression analysis. Boxplots represent 25%, 50%, and 75% quantiles. ABCB1 = ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 1; ACKR1 = atypical chemokine receptor 1; AEC = arterial endothelial cell; CA4 = carbonic anhydrase 4; CCL21 = C-C motif chemokine ligand 21; CLDN5 = claudin 5; COL15A1 = collagen type XV α 1 chain; CPE = carboxypeptidase E; DKK2 = Dickkopf WNT signaling pathway inhibitor 2; EDNRB = endothelin receptor type B; ERK = extracellular signal-related kinase; FAK = focal adhesion kinase; FCN3 = ficolin 3; FOXF1 = forkhead box F1; GA = gestational age; GJA5 = gap junction protein α 5; GTPase = guanosine triphosphatase; HPGD = 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase; ID1 = inhibitor of DNA binding 1; KIT = KIT proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase; LEC = lymphatic endothelial cell; MAPK = mitogen-activated protein kinase; PECAM1 = platelet and endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1; PROX1 = Prospero homeobox 1; PTEN = phosphatase and tensin homolog; snRNA-seq = single-nucleus RNA sequencing; SLC6A4 = solute carrier family 6 member 4; STAT3 = signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; SVEC = systemic vascular endothelial cell; VEC = venous endothelial cell.