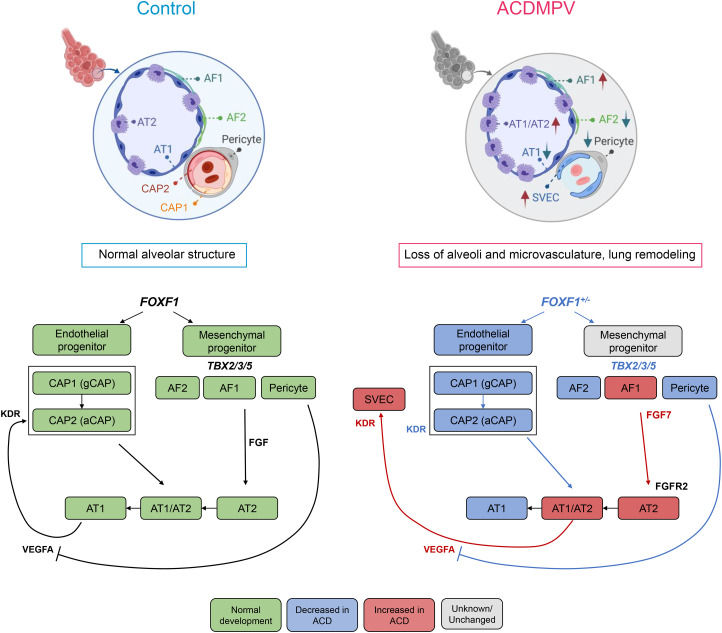
Figure 8.
Schematic showing alveolar structure and cell–cell communications in normal human lung and alterations in alveolar capillary dysplasia with misalignment of pulmonary veins (ACDMPV). FOXF1 (forkhead box F1) is expressed in pulmonary mesenchymal cells, including fibroblasts, pericytes, and endothelial cell (EC) progenitors. FOXF1 was required for the differentiation or survival of endothelial and fibroblast progenitors, which in turn influence the growth and differentiation of the pulmonary epithelial progenitors during the formation of the peripheral lung. FOXF1 deficiency in ACDMPV disrupted gene expression in EC progenitors, preventing differentiation or survival of CAP2 ECs, critical for the formation of the alveolar gas exchange, resulting in hypoxemia at birth. Increased expression of VEGFA by atypical alveolar epithelial progenitors (AT1/AT2) is likely to enhance the proliferation and migration of the systemic vasculature (SVECs), a characteristic of ACDMPV. aCAP = aerocyte capillary cell; ACD = alveolar capillary dysplasia; AF1 = alveolar fibroblast 1; AF2 = alveolar fibroblast 2; AT1 = alveolar type 1 cell; AT1/AT2 = AT1/AT2 transitional cell; AT2 = alveolar type 2 cell; CAP1 = capillary 1; CAP2 = capillary 2; FGFR = fibroblast growth factor receptor; gCAP = general capillary; KDR = kinase insert domain receptor; SVEC = systemic vascular endothelial cell; TBX = T-box transcription factor; VEGFA = vascular endothelial growth factor A.