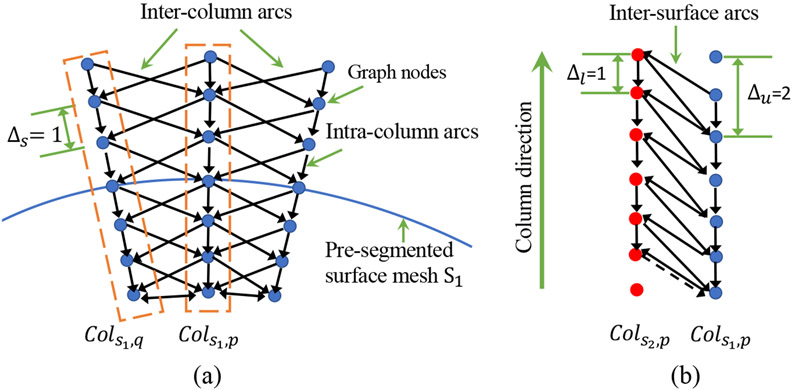
Figure 5:
Geometric constraints in graph construction. (a) Inter-column and intra-column arcs link graph nodes from columns built along the column direction through the pre-segmented surface mesh . Each mesh vertex is associated with a column of nodes and and represent the coordinates of the mesh vertices where columns are built. Columns located in the same triangle polygon are neighboring columns. The inter-column arcs are deployed between neighboring columns to enforce surface smoothness constraints . (b) Inter-surface arcs model the separation constraint between the two interacting surfaces and . The column from interacts with from and and restrict the minimum and maximum distances between the surface-connected nodes of the two columns, respectively. Best viewed in color.