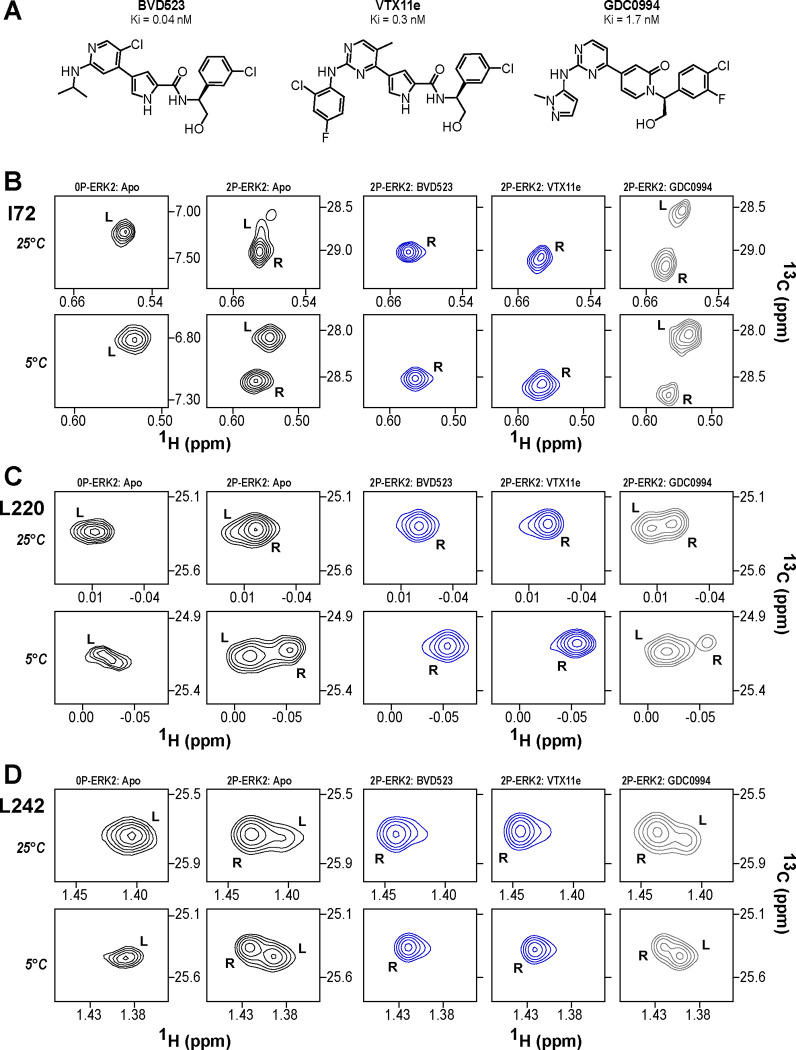
Figure 1. BVD523 and VTX11e stabilize the R-state in 2P-ERK2.
(A) Chemical structures of the ATP-competitive ERK1/2 inhibitors, BVD523, VTX11e and GDC0994. (B-D) 2D-HMQC spectra collected at 25°C and 5°C ([ERK2]:[inhibitor] = 1.0:1.2), showing [methyl-13C,1H] peaks of residues (B) I72, (C) L220 and (D) L242, which report R and L conformers. Their locations in the ERK2 structure are shown in Suppl. Fig. S1. 2P-ERK2 complexed with BVD523 and VTX11e (shown in blue) shift to 100% R at all temperatures, while 2P-ERK2 complexed with GDC0994 (shown in grey) retains conformational exchange between R:L populations of 80:20, similar to the apoenzyme. Previous studies show that 0P-ERK2 complexed with all inhibitors retains the L conformer seen in the apoenzyme (Pegram et al., 2019). Full NMR spectra are shown in Suppl. Fig. S2. Titration of 2P-ERK2 with VTX11e and GDC0994 to demonstrate binding saturation is shown in Suppl. Fig. S3.