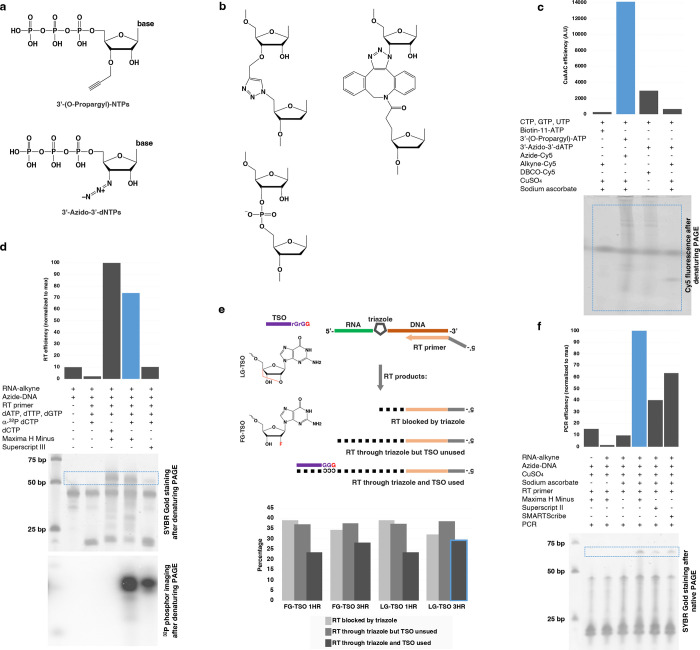
Extended Data Fig. 1 |. click-chemistry mediated nascent RNA conjugation to single-stranded DNA and optimization of reverse transcription.
a, Click-chemistry compatible nucleotides tested in AGTuC development. A few nucleotide triphosphates were custom synthesized or sourced with few properties in mind - smaller size, chain termination ability, and the possibility of incorporation by native RNA polymerases. b, Structure of the triazole linkage formed by CuAAC between the nascent-RNA terminally labeled with 3’-(O-Propargyl)-NTPs and the azide-labeled DNA (top left), the linkage formed by SPAAC between the nascent-RNA terminally labeled with 3’-Azido-3’-dNTPs and DBCO DNA (right). The phosphodiester linkage in a native oligonucleotide is shown for comparison (bottom left). c, Incorporation efficiency of 3’-(O-Propargyl)-ATP or 3’-Azido-3’-dATP by native RNA polymerase in nuclear run-on reaction. The propargyl or azide labeled nascent RNA is clicked with Cy5 via CuAAC (Azide-Cy5 or Alkyne-Cy5) or SPAAC (DBCO-Cy5), resolved in a denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE), and quantified by measuring the Cy5 fluorescent from the gel image. The blue dotted line represents the gel region that was quantified. d, Relative quantification of reverse transcription (RT) efficiency of two commercial enzymes traversing through the triazole link formed between the alkyne-labeled RNA and azide-labeled DNA by CuAAC. RT was performed in the presence of either native dCTP or radioisotope a-32P dCTP, and the RT reaction was resolved in denaturing PAGE and imaged sequentially for nucleic acid signal (top gel) and radioisotope signal (bottom gel). e, Quantification of aborted intermediate and completed desired products (RT through triazole and TSO used) formed during the one hour or three hours of RT using TSO with terminal Locked-Nucleic-Acid-Guanosine (LG) or 2’-Fluoro-Guanosine (FG). f, Confirmation and relative quantification of CuAAC, RT, and PCR of clicked product formed between the alkyne-labeled RNA and azide-labeled DNA by three commercial Reverse transcriptase enzymes. Note: The blue bar, line, or border represents the “winner” condition.