Figure 2: CRISPRa with PAM-flexible dCas9 variants.
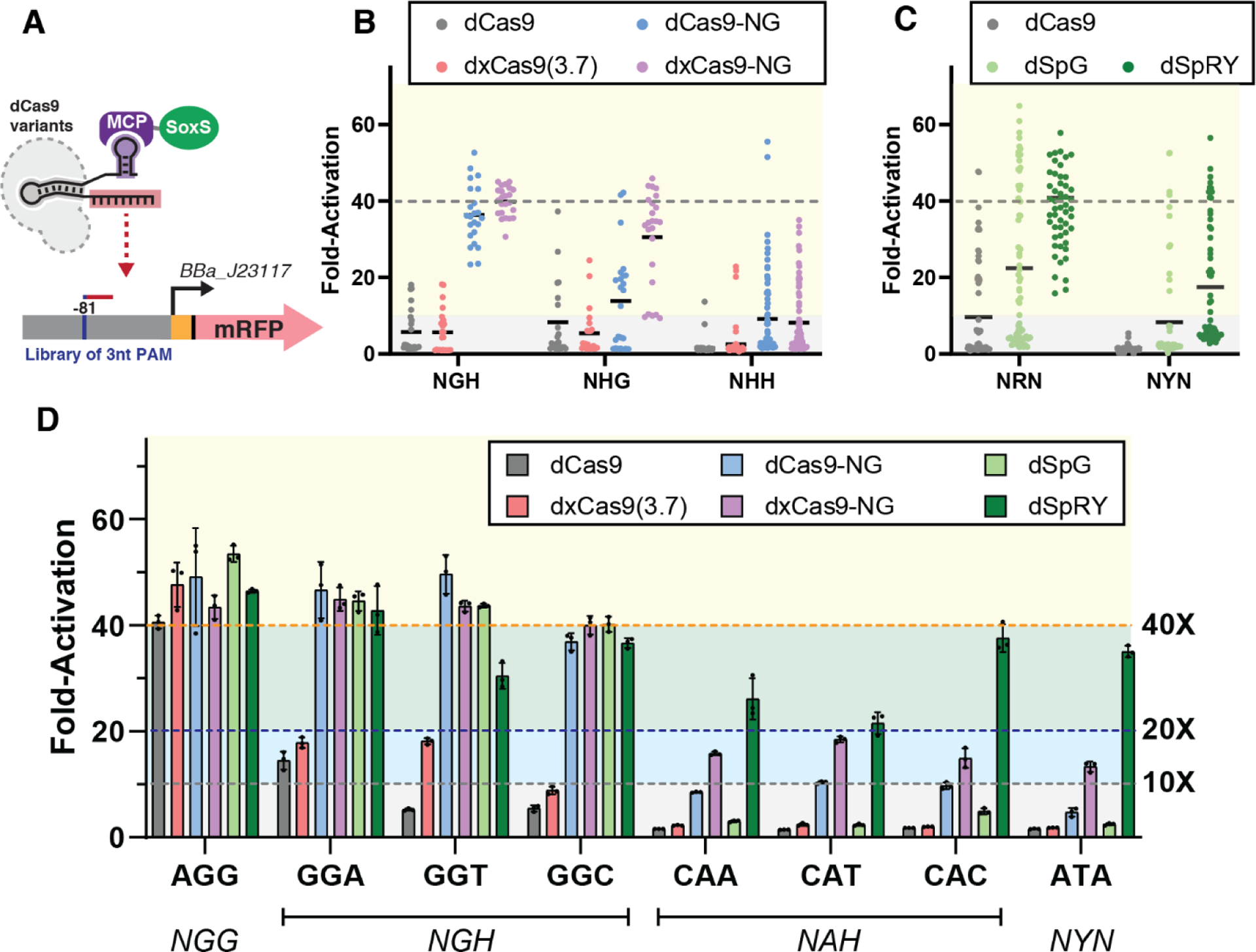
(A) CRISPRa for PAM-flexible dCas9 variants was tested on an mRFP reporter gene with libraries of alternative 3 nucleotide PAMs at the −81 target site. (B) Reporter gene expression with the dxCas9-NG group (Figure 1A) at NGH, NHG, and NHH PAM libraries. dxCas9-NG outperforms other variants in every PAM library. (C) Reporter gene expression with the dSpRY group (Figure 1A) at NRN and NYN PAM libraries. dSpRY exhibited the highest CRISPRa efficiency. (D) Direct comparisons of reporter gene expression with dCas9, dxCas9(3.7), dCas9-NG, dxCas9-NG, dSpG, and dSpRY at a representative set of PAMs. dCas9-NG, dxCas9-NG, and dSpRY performed best at NGN PAMs while dSpRY outperformed other variants at NAN and NYN PAMs. An scRNA targeting the J306 sequence was used for all library screens and individual PAM assays. To calculate fold-activation, we used an off-target scRNA (hAAVS1) with an AGG PAM reporter to define the basal expression level. Basal reporter expression levels vary <1.5-fold with different dCas9 variants or PAMs (Figure S5). Values in panel D represent the mean ± standard deviation calculated from n = 3.
