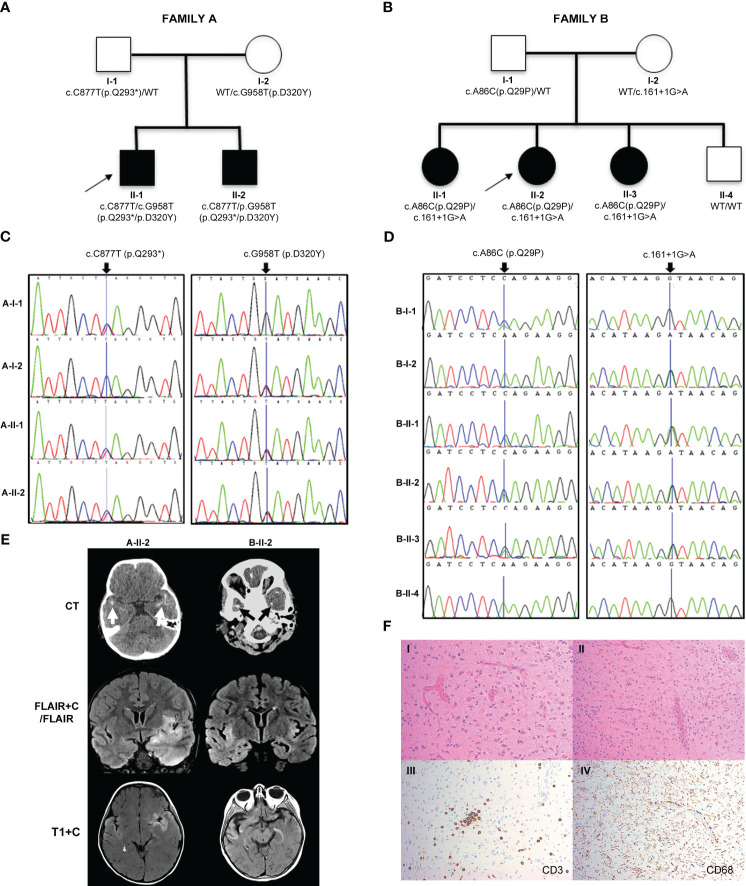
Figure 1.
Pedigrees, genetic analysis, neurological features and shedding assay results in families A and B. (A, B) Pedigrees of family A and family B, respectively, with black shapes showing affected children, white shapes showing unaffected parents and children and arrows indicating the proband of each family. Genetic testing revealed that the affected children in family A were compound heterozygous for IRAK4 gene mutations c.C877T (p.Q293*) and c.G958T (p.D320Y) and in family B were compound heterozygous for IRAK4 gene mutations c.A86C (p.Q29P) and c.161 + 1G>A. Parents in both families were found to be heterozygotes. (C) Sanger sequencing electropherograms for family A showing the c.C877T (p.Q293*) variant inherited from the father (A-I-1), and c.G958T (p.D320Y) variant inherited from the mother (A-I-2). (D) Sanger sequencing electropherogram for family B showing c.A86C (p.Q29P) variant inherited from the father (B-I-1), and c.161 + 1G>A variant inherited from the mother (B-I-2). (E) Brain imaging. Left column (A-II-2): Axial CT scan showing bitemporal subcortical calcification (arrows). Post-contrast coronal FLAIR (FLAIR+C) and axial T1-weighted (T1+C) MRI sequences, showing asymmetrical swelling, signal abnormality and cortical-subcortical contrast enhancement in temporal lobes, insular and basal frontal regions. Right column (B-II-2): CT scan showing patchy subcortical calcification in the temporal lobes bilaterally (arrows). Coronal MRI FLAIR demonstrates asymmetrical signal abnormality involving the insular regions and temporal lobes. Post-contrast T1-weighted (T1+C) MRI performed after 3 months shows persisting cortical and subcortical contrast enhancement with signal abnormality in the temporal lobes and the frontal basal regions. (F) Brain biopsy of B-II-2 showing disruption of the cortical architecture with interspersed reactive astrocytes in keeping with gliosis (I); blood vessels with reactive endothelium and scattered mononuclear chronic inflammation (II); scattered CD3 positive T lymphocytes (III); diffuse microglial upregulation with interspersed macrophages (IV).