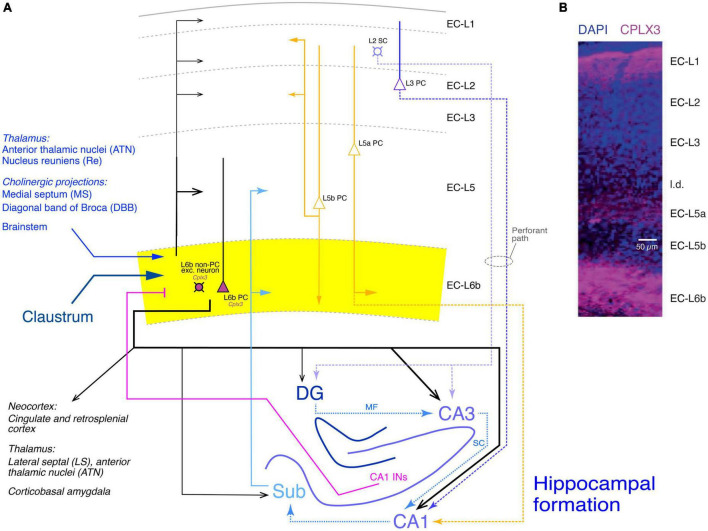
FIGURE 7.
Synaptic connectivity of layer 6b of the entorhinal cortex (EC-L6b). (A) Simplified diagram of the EC-L6b synaptic input and output circuitry. EC-L6b neurons are outlined in black with purple cell bodies to indicate that they express Cplx3. EC-L6b excitatory neurons project through the EC and to the hippocampal formation, in particular to the CA3 region. To put the role of the EC-L6b to the hippocampus connections into context, the circuitry of the hippocampal formation is also shown in this figure. Different hippocampal regions, the excitatory axonal projections within the hippocampus, between EC-L2 and EC-L3 and the hippocampus (perforant pathway with EC-L2 to DG and CA3 and EC-L3 to CA1), and from the hippocampus back to EC-L6b are color-coded in different shades of blue. CA1 interneuron (CA1 INs) to EC-L6b projections are given in magenta. Other inputs to EC-L6b (from the thalamus, cholinergic regions, brainstem, and claustrum are shown in hues of dark blue. Furthermore, the recently identified L5a PC projections to CA1 (Tsoi et al., 2022) are also included and color-coded in yellow; EC-L5a PCs provide also the major intrinsic input to EC-L6b. Albeit closer to layer 6b, input from EC-L5b PCs to EC-L6b is sparse but strong in all other layers (Ohara et al., 2018). DG, dentate gyrus; Sub, subiculum; MF, mossy fibers; SC, Schaeffer collaterals. Arrow thickness signifies connection strength. Different arrow heads signify: ➤ synaptic connections not involving EC layer 6b; ▶ synaptic input to layer 6b; >synaptic output from EC layer 6b. (B) Layers of the entorhinal cortex (EC) revealed with DAPI and complexin 3 (CPLX3) immunostaining. the entire layer 6 is labeled by the subplate/L6b marker CPLX3 suggesting that entire EC-L6 corresponds to layer 6b in the neocortex. Modified after Ben-Simon et al. (2022) under a CC license.