FIGURE 8.
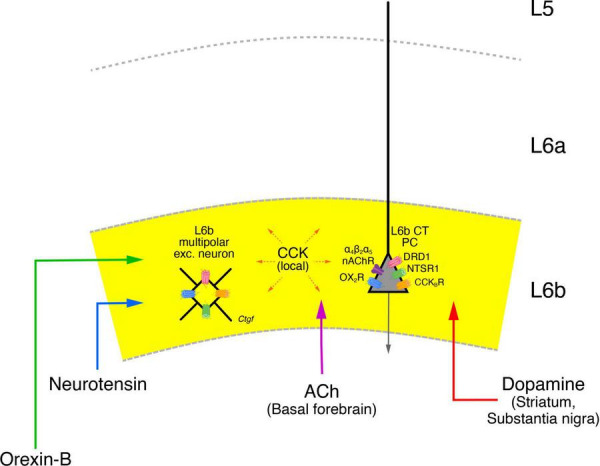
Neuromodulatory influence on layer 6b neurons. Layer 6b is under tight control of neuromodulators such as the neuropeptides Orexin-B (green), Neurotensin (blue), Cholecystokinin (CCK, orange) as well as acetylcholine (ACh, violet) and dopamine (red) all of which produce direct depolarizing responses in L6b excitatory neurons. The brain regions from which a particular neuromodulator is released are given in brackets under the name of the neuromodulator. The brain regions from which orexinergic and neurotensinergic afferents entering layer 6b originate are not clearly known and have therefore been omitted here. CCK is released from neurons in the neocortex both in layer 6b but also from other cortical layers. The names of the neuromodulator receptors are given next to the receptor drawing; apart from the nAChRs all receptor types are G-proteins (see text for details). The release of orexin in the lateral hypothalamus is under the control of neurotensin which promotes their activity. Orexinergic neurons control the release of ACh and dopamine in the basal forebrain and the VTA-SNc complex, thereby exerting also an indirect control over cortical activity, in addition to the more direct modulatory role in layer 6b. In addition, cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain are also innervated by VTA-SNc dopaminergic neurons; these neurons receive also cholinergic input put from brainstem nuclei and not the nasal forebrain. These and other details in the network of the neuromodulatory systems shown here have omitted for clarity.
