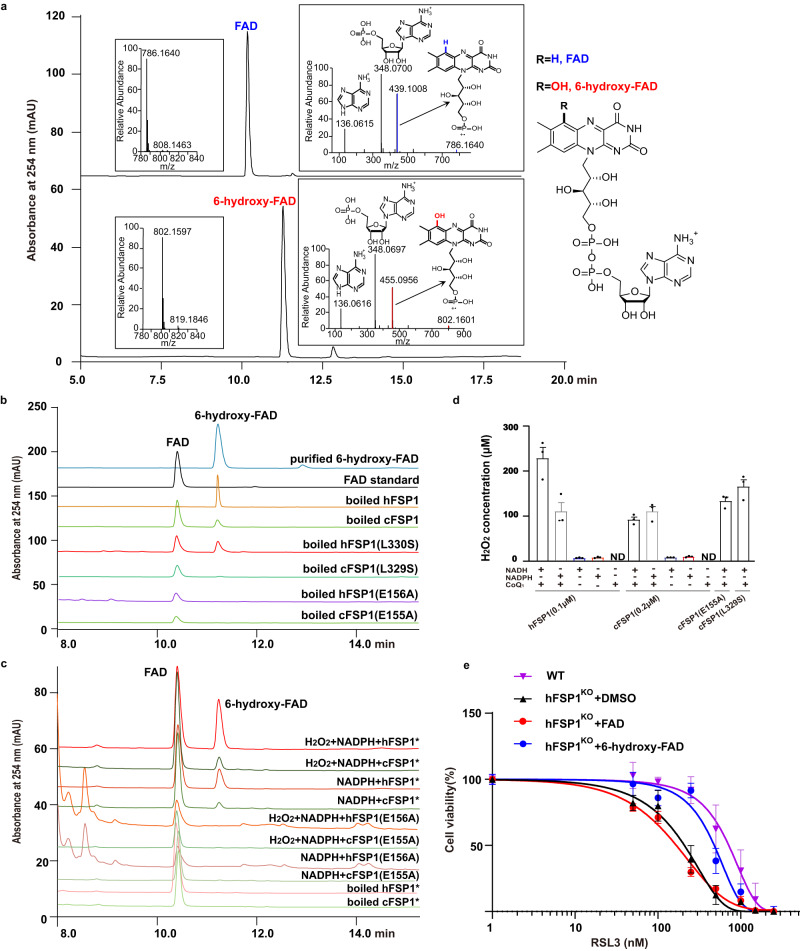
Fig. 5. FSP1 also generate 6-hydroxy-FAD to block ferroptosis.
a HPLC-MS/MS chromatogram of the commercial FAD (upper) and the purified 6-hydroxy-FAD (lower). The left insert panels show the MS spectra, the ions at m/z 786.1640 and 802.1597 represent the [M + H]+ ion of FAD and 6-hydroxy-FAD, respectively. The right insert panels show the tandem mass spectra resulting from higher-energy collision dissociation (HCD) of the precursor ions ([M + H]+ = 786.16) and ([M + H]+ = 802.16). The assigned fragments are represented in the spectra, the chemical structure of FAD and 6-hydroxy-FAD are shown in the right part. b HPLC analysis of standard FAD (black), purified 6-hydroxy-FAD (blue) and the indicated protein samples. c HPLC analysis of the reaction mixtures of the indicated proteins (100 μM) with NADPH or with NADPH and H2O2, * represent the FAD-reconstituted protein. d The indicated FSP1 proteins simultaneously catalyze the reduction of CoQ1 and generate hydrogen peroxide in the presence of NADPH and oxygen, ND, not detected. e Dose response of RSL3-induced cell death of HT1080 wild-type (WT) cells and HT1080 hFSP1KO cells treated with DMSO, 10 μM FAD or 6-hydroxy-FAD. Cell viability was assessed using CCK8 assay. The experiments in a, b, and c were performed only once, respectively. Data in d and e represent the mean ± s.e.m. of three experiments (n = 3). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.