Fig. 3. C9orf72 mutant iPSC microglia are pro-inflammatory with consistently upregulated expression and release of MMP9.
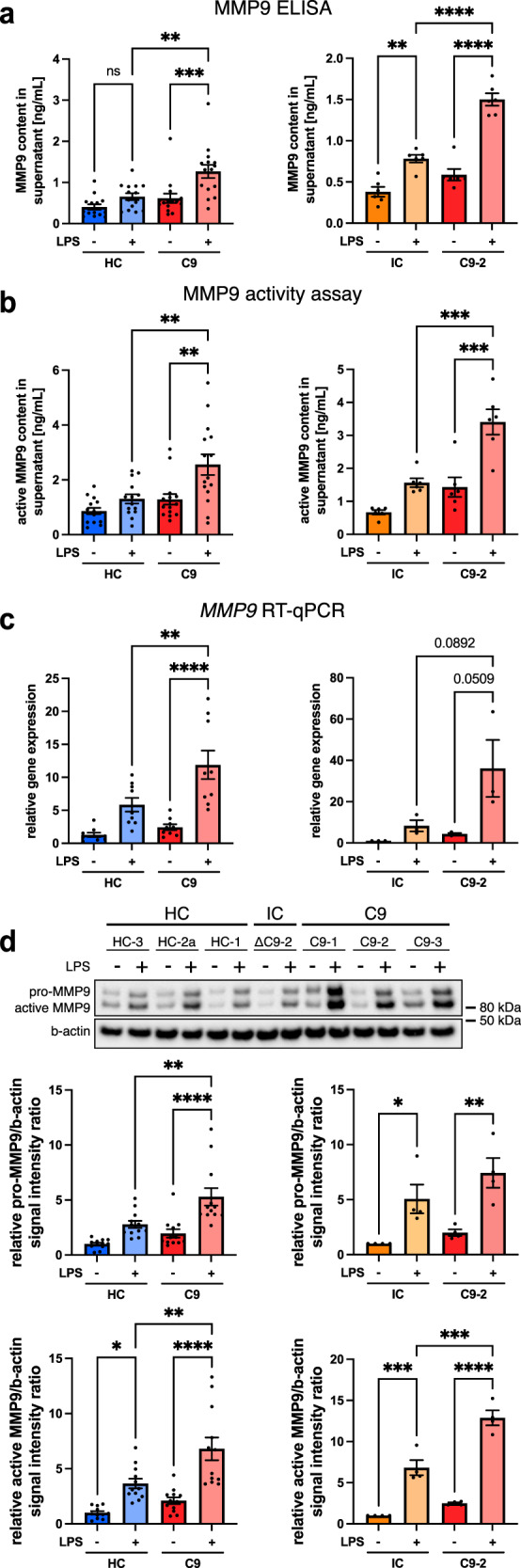
a ELISA quantification of MMP9 in supernatants from unstimulated and LPS-stimulated healthy control (HC), isogenic control (IC), and C9orf72 mutant (C9) microglia in monoculture (pMGL) shows significantly increased MMP9 release in the C9-HC (n = 3 lines per condition, n = 5 differentiations each) and IC-C9-2 pMGL comparisons (n = 1 line per condition, n = 6 differentiations each). b Fluorometic activity assay for active MMP9 in supernatants from unstimulated and LPS-stimulated HC, IC, and C9 pMGL shows significantly increased MMP9 activity in the C9-HC (n = 3 lines per condition, n = 5 differentiations each) and IC-C9-2 pMGL comparison (n = 1 line per condition, n = 6 differentiations each). c RT-qPCR for MMP9 expression in unstimulated and LPS-stimulated HC, IC, and C9 pMGL normalized to the housekeeping gene TBP showing significantly increased MMP9 expression in the C9-HC (n = 3 lines per condition, n = 3 differentiations each) and numeric increase in IC-C9-2 pMGL comparison (n = 1 line per condition, n = 3 differentiations each). d Top: exemplar Western blot against the pro-form and active form of MMP9 in unstimulated and LPS-stimulated HC, IC, and C9 pMGL. Bottom: quantification shows significantly increased expression of pro-MMP9 in the C9-HC pMGL comparison and a numeric increase in the IC-C9-2 pMGL comparison. Active MMP9 is significantly increased in both comparisons. Both normalized to the housekeeping gene b-actin (n = 3 lines per condition for C9-HC comparison, n = 1 line for the IC-C9-2 comparison, n = 4 differentiations each). Single data points and means ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test (a–d). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
