Fig. 6. C9orf72 mutant iPSC microglia cause non-cell-autonomous toxicity to co-cultured healthy iPSC motor neurons after prolonged LPS treatment via an MMP9-dependent mechanism.
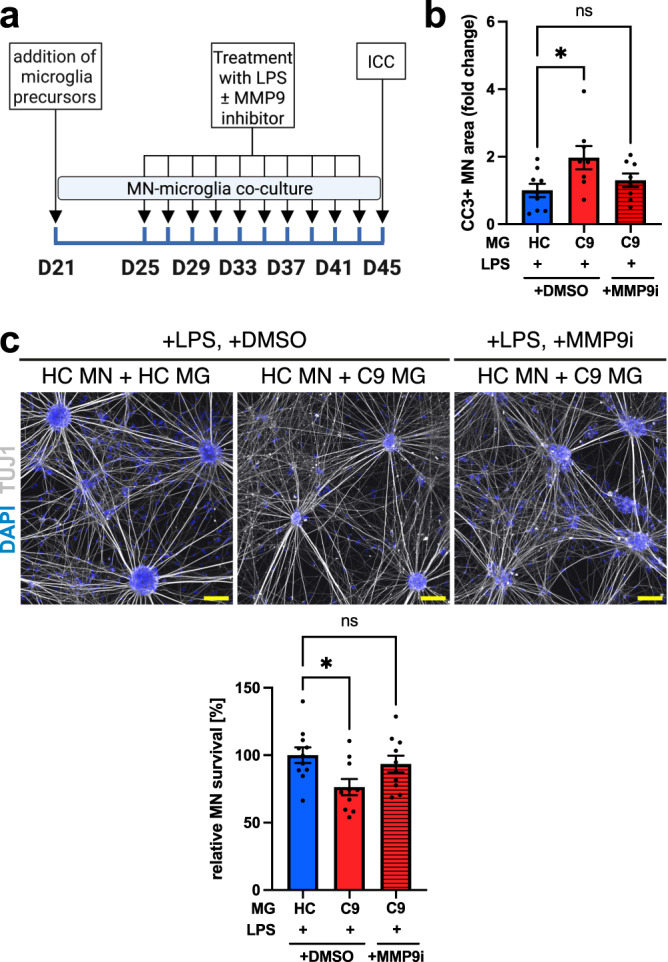
a Experimental setup for experimental setup for prolonged treatment of motor neuron (MN)-microglia (MG) co-cultures with LPS. b Quantification showing significantly increased relative fold change in cleaved caspase 3 (CC3) expression in co-cultures of healthy control (HC) MNs with C9orf72 mutant (C9) MG compared with HC MG after prolonged LPS treatment. Treatment with MMP9 inhibitor 1 (3 μM, MMP9i) ameliorates microglial neurotoxicity (n = 3 microglial lines per genotype, n = 3 differentiations). c Top: exemplar images showing co-cultures of HC MNs with HC and C9 MG after pro-longed LPS treatment. Bottom: quantification showing significantly reduced relative MN survival in co-cultures of HC MNs with C9 MG compared with HC MG after prolonged LPS treatment. Treatment with MMP9i ameliorates microglial neurotoxicity (n = 3 microglial lines per genotype, n = 4 differentiations). Scale bars: 100 μm. Single data points and means ± SEM. *P < 0.05; ns: not significant. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test (b, c). The graphics for panel a were created using Biorender.com. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
