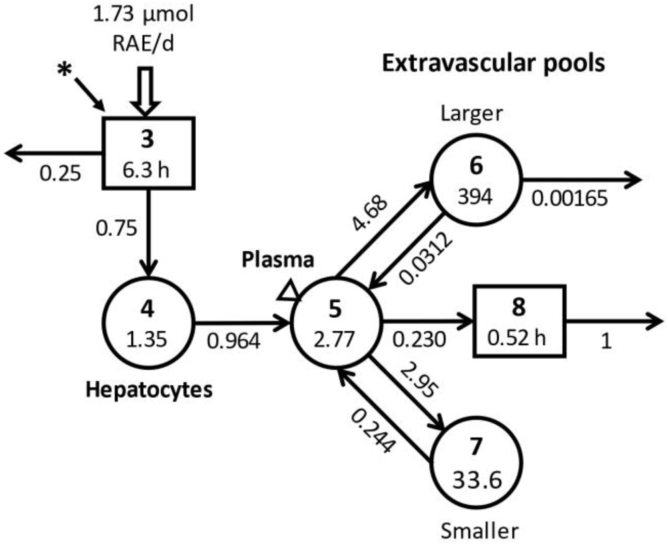
FIGURE 1.
Compartmental model for vitamin A metabolism in humans, with results obtained by modeling the composite SCD-HbSS dataset. The model is from [25]. Circles represent compartments, the rectangles are delay components, and arrows are fractional transfer coefficients [L(I,J)s, or the fraction of retinol in compartment J transferred to compartment I each day]; delay times [DT(I)s] correspond to the time (h) spent in delay component I. Delay component 3 is the site of input of tracer (∗) and dietary vitamin A, as well as the site of loss of unabsorbed vitamin A; it represents the processes of digestion and absorption of ingested vitamin A and then its packaging into chylomicrons and their subsequent metabolism until uptake of chylomicron remnants by hepatocytes (compartment 4). Retinol in hepatocytes is secreted into plasma compartment 5 bound to retinol-binding protein; plasma retinol is either irreversibly transferred to component 8 for rapid utilization by tissues or it exchanges with vitamin A in 2 extravascular pools (a larger compartment 6 and a smaller compartment 7, the sum of which is TBS). Irreversible loss from the system occurs from compartment 6 and component 8. During modeling, L(4,3) and L(0,3) were fixed to reflect 75% absorption efficiency and 25% of incoming vitamin A not absorbed; DT(8) was fixed at 75 min; and following WinSAAM convention, L(0,8)=1. Also, L(8,5) was calculated assuming that 50% of the disposal rate was from transfer of retinol from plasma to component 8; this was fixed in the model and the value for L(0,6) was constrained to reflect the remaining 50% of disposal rate coming from the larger extravascular pool. Final steady state model predictions for fractional transfer coefficients (d−1) are shown with each arrow and those for delay times are indicated in the rectangles; retinol pool sizes (i.e., compartment retinol masses; μmol) are shown for each compartment. RAE, retinol activity equivalents; SCD-HbSS, sickle cell disease hemoglobin SS type; TBS, vitamin A total body stores; WinSAAM, Windows version of Simulation, Analysis and Modeling software.