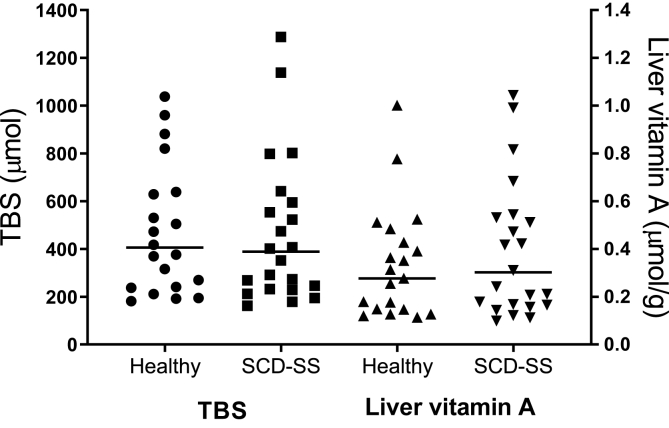
FIGURE 3.
Predictions of TBS and liver vitamin A concentration for healthy young people (n = 20) and subjects with SCD-HbSS before vitamin A supplementation (n = 22). Symbols are predictions for individual subjects at 3 d (except that 1 healthy subject was done at 5 d); lines are geometric means for each group. Values for TBS were calculated using Equation 1 (see Methods), with group values for the equation’s composite coefficient FaS calculated by modeling the SCD-HbSS pre-supplementation super-subject dataset along with each subject’s SAp at the corresponding time. Model-predicted values for FaS used in these calculations were 2.40 at 3 d and 1.34 at 5 d. Liver vitamin A concentration was estimated as TBS (μmol) × fraction of TBS in the liver / estimated liver weight (g), assuming that 80% of TBS was in the liver [40] and calculating liver weight using the regression equation in [41]. RID, retinol isotope dilution; SAp, plasma retinol specific activity; SCD-HbSS, sickle cell disease hemoglobin SS type; TBS, vitamin A total body stores.