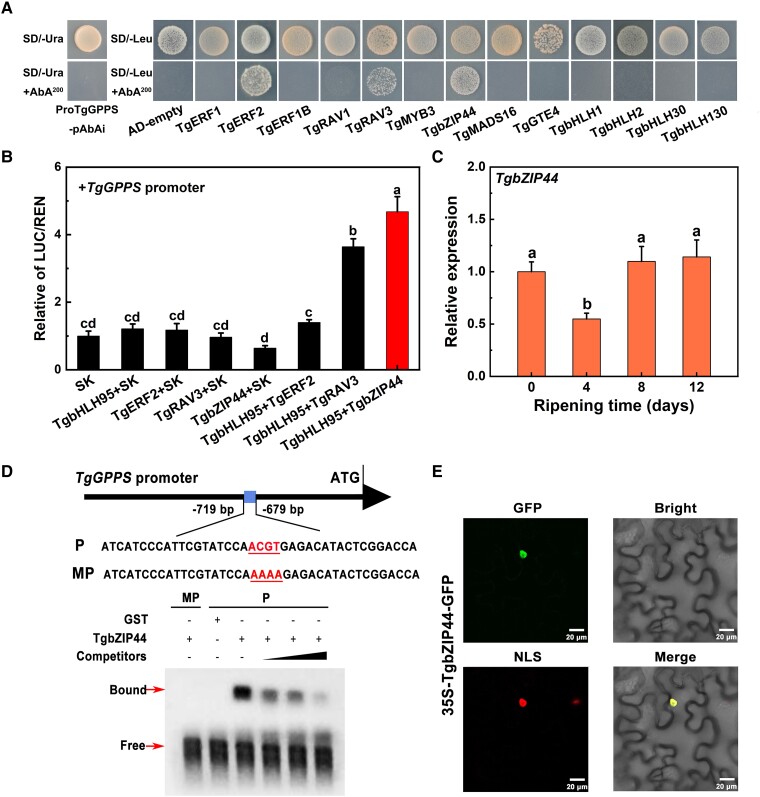
Figure 5.
Functional characterization of TgbZIP44. A) Yeast 1-hybrid analysis of other TFs binding capacity to the TgGPPS promoter, with the empty vector pGADT7 (AD) used as a negative control. B) Synergistic transactivation effect of different TFs on the TgGPPS promoter. The LUC/REN ratio of the empty vector (SK) plus the promoter was used as a calibrator (value set to 1.0). Error bars represent Se based on 3 biological replicates. The different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) by Duncan's multiple range test. C) The TgbZIP44 expression pattern in xiangfei nuts during the postharvest ripening stage. Error bars represent Se based on 3 biological replicates. The different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) during the postharvest ripening stage by Duncan's multiple range test. D) In vitro binding ability of TgbZIP44 to the TgGPPS promoter performed by EMSA. The presence (+) or absence (−) of specific probes is marked. The black arrows become larger from left to right indicating an increase in the concentration of competitive probes. GST protein was used as a negative control. E) Subcellular localization analysis of TgbZIP44. The fluorescent signals were detected in tobacco cells cotransfected with TgbZIP44-GFP and the nuclear RFP-NLS marker. Scale bar = 20 μm.