FIG. 6.
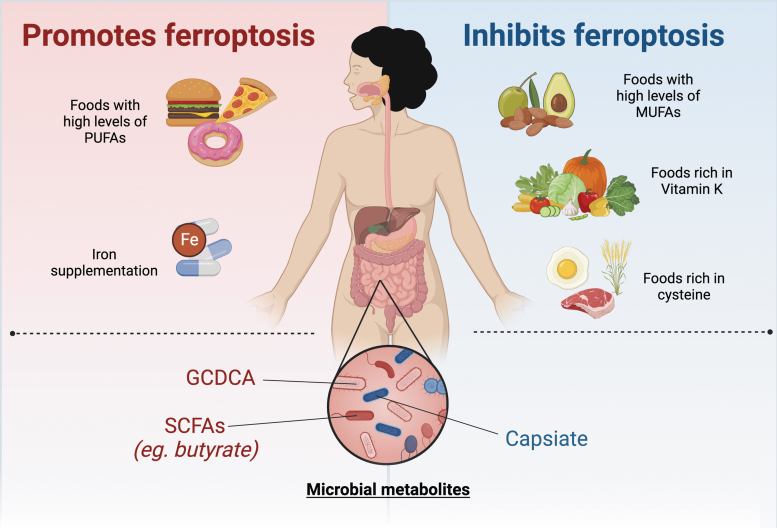
Nonpharmacological effects on ferroptosis. Diet and microbiota have been shown to affect ferroptosis. Diets rich in PUFAs and iron supplementation promote ferroptosis, while diets rich in MUFAs, cysteine, and vitamin K inhibit ferroptosis. Gut dysbiosis affects ferroptosis in a context-dependent manner. Some microbial metabolites (GCDCA, SCFAs) have been reported to inhibit ferroptosis, while other microbial metabolites (capsiate) are able to protect against ferroptosis. GCDCA, glycochenodeoxycholate; MUFA, monounsaturated fatty acid; SCFA, short-chain fatty acid.