Figure 7. Overview of antimicrobial resistance determinants in the cell envelope.
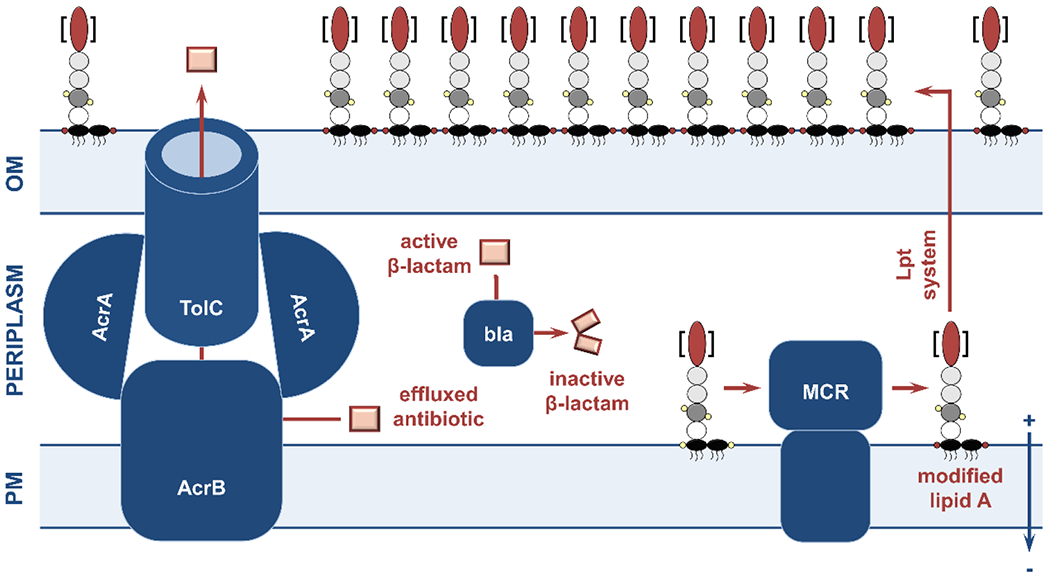
(left) Expression or upregulation of efflux pumps results in resistance to multiple antibiotic classes. The E. coli tripartite AcrAB-TolC pump depicted here is a typical Resistance-Nodulation-Division (RND) pump that extrudes fluoroquinolones, macrolides, and β-lactams from the periplasm to the extracellular milieu. (center) Soluble β-lactamase enzymes competitively bind β-lactam antibiotics in the periplasm and hydrolyze their essential four membered β-lactam ring, therefore preventing inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis. (right) During LPS synthesis, the phosphate moieties (small yellow circles) of lipid A (black ovals) are modified by mobile colistin resistance (MCR) proteins (phosphoethanolamine addition is depicted by red circles on the lipid A component). This, in turn, reduces the overall charge of the outer membrane and obstructs the activity of last-line polymyxin antibiotics. OM, outer membrane; PM, plasma membrane.
