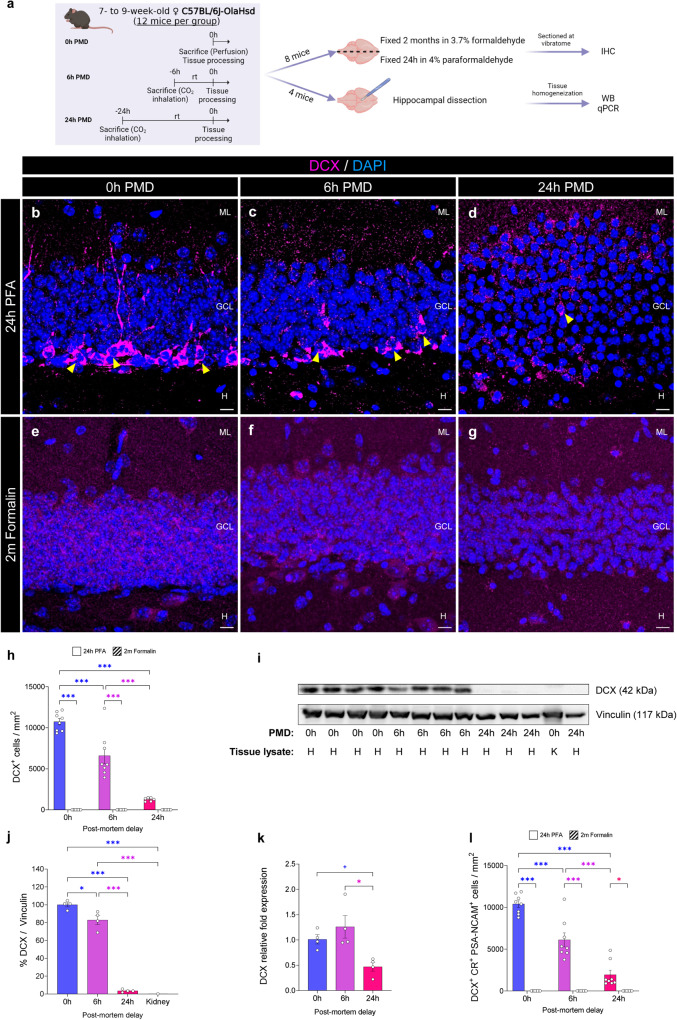
Fig. 1. Impact of the post-mortem delay (PMD) and fixation time on the detection of immature dentate granule cells (DGCs).
a Experimental design. b–g Representative images of Doublecortin (DCX) staining under distinct experimental conditions. A guinea pig anti-DCX antibody (Synaptic Systems #326004#) was used. h Density of DCX+ immature DGCs detected with a guinea pig anti-DCX antibody (Synaptic Systems #326004#). i, j Normalized levels of DCX protein detected by western blot (WB) analysis. k Normalized levels of DCX mRNA expression detected by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). l Density of triple-labeled DCX+ Calretinin (CR)+ Polysialylated-neural cell adhesion molecule (PSA-NCAM)+ immature DGCs detected. In a, the illustration was created with BioRender.com. In b–g, Z-projection images are shown. IHC immunohistochemistry. ML Molecular layer. GCL Granule cell layer. H Hilus. In i, H hippocampus, K kidney. White scale bar: 10 μm. Yellow triangles: DCX+ immature DGCs. Graphs represent mean values ± SEM. In h and l: n = 8 mice. In j, k n = 4 mice. + 0.1 > p ≥ 0.05; *0.05 > p ≥ 0.01; and ***p < 0.001.