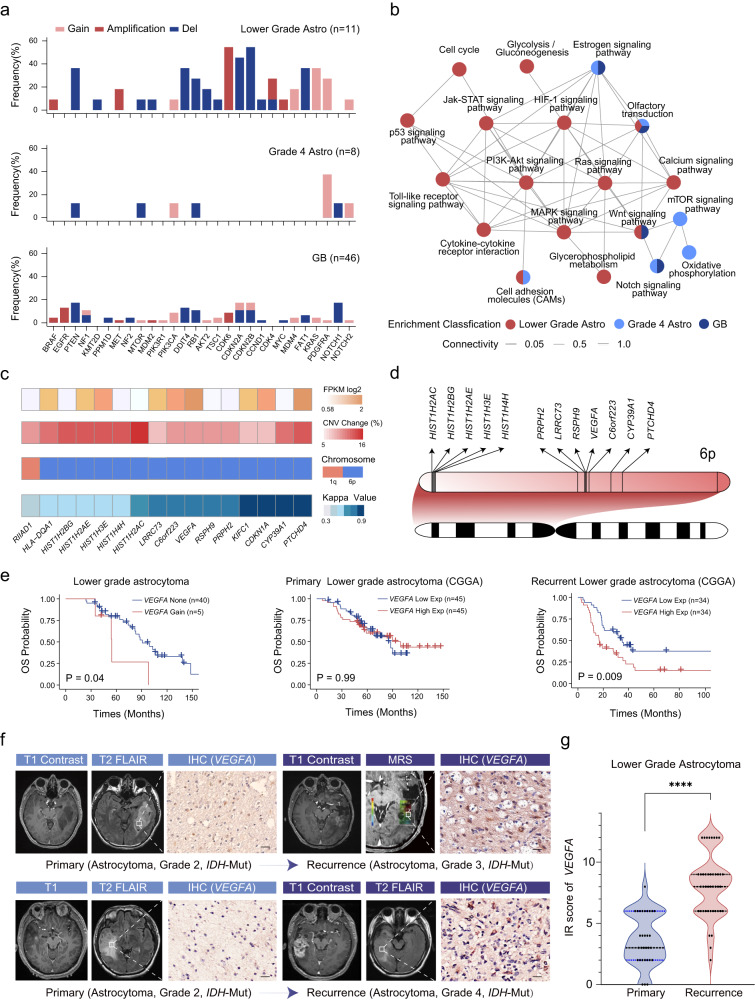
Fig. 4. Candidate driver genes and cancer-related pathways during the relapse of lower grade astrocytoma, grade 4 astrocytoma and GB.
a Newly acquired canonical driver gene alterations during the relapse of lower grade astrocytoma, grade 4 astrocytoma and GB. Horizontal axis represents driver gene, and vertical axis represents the proportion of alterations in all samples. Dark red color represents amplification, light red represents gain, and blue represents deletion. b Enrichment network of cancer related KEGG pathways during the relapse of lower grade astrocytoma, grade 4 astrocytoma and GB. Each circle represents one pathway. Circles in red, light blue and dark blue represent they were enriched in lower grade astrocytoma, grade 4 astrocytoma and GB, respectively. Circles with multiple colors represents they were enriched in multiple groups. c Profiling of 16 genes with consistent transcriptional and CNV changes in 1q and 6p. Expression profile, CNV alteration frequency, chromosome arm status, and kappa value between chromosome arm and gene alteration were showed from the top to the bottom panel. Expression data was download from CGGA database and public CNV data was from cBioPortal database. Orange color represents up-regulated genes on the top of the panel. Red color represents gain on the middle of the panel. d Location of the 12 prognosis-related genes in 6p. The genomic coordinate increase from left to the right of the panel. Line of each gene represents its position in the chromosome arm. e Overall survival for lower grade astrocytoma patients with or without VEGFA gain (5 patients from this study, 40 patients from cBioPortal), recurrent lower grade astrocytoma patients with high expression of VEGFA and low expression of VEGFA, primary lower grade astrocytoma patients with high expression of VEGFA and low expression of VEGFA. P values were obtained from the log-rank test. f IHC staining of VEGFA and MRI images on paired primary and recurrent glioma. Patient 1 was initially diagnosed with a lower grade astrocytoma (IDH-mutant, grade 2 astrocytoma) in 2009 with T1 and T2 FLAIR imaging showing a temporal lesion. In 2016, the tumor recurred as a grade 3 astrocytoma (IDH-mutant), and T1 contrast imaging revealed tumor enhancement and a high Cho/NAA ratio. Patient 2 was initially diagnosed with a lower grade astrocytoma (IDH-mutant, grade 2 astrocytoma) in 2010 with T1 and T2 FLAIR imaging showing a temporal lesion. In 2012, the tumor recurred as a grade 4 astrocytoma (IDH-mutant), and T1 contrast imaging revealed tumor enhancement. g The mean immunoreactivity score (IRS score) of VEGFA was compared between primary and recurrent gliomas. P values was obtained from the Wilcoxon rank-sum test.