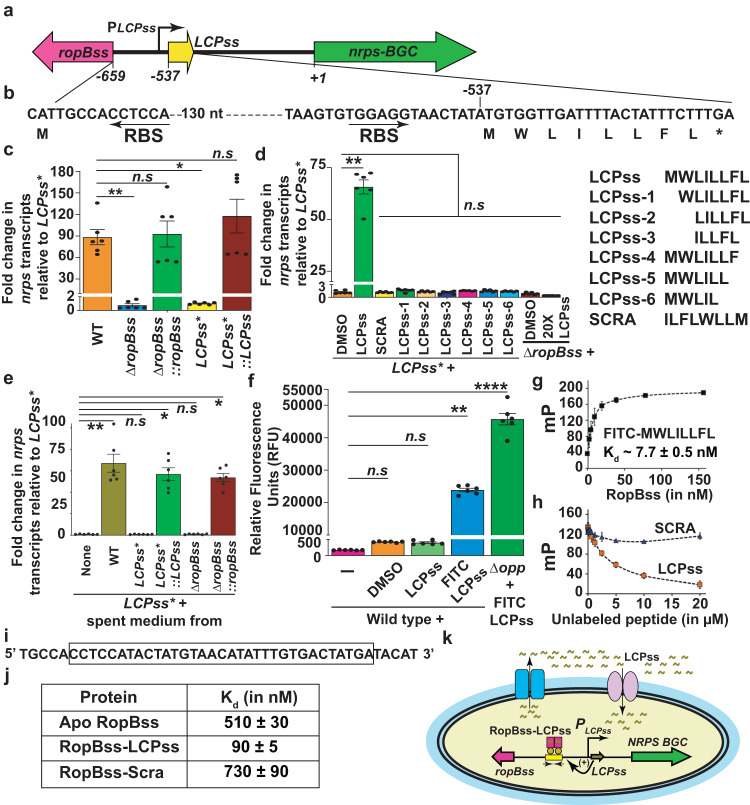
Fig. 4. Intercellular signaling and gene regulation by S. salivarius LCP.
a Schematic representation of genetic elements in S. salivarius (ss) encoding ropBss, LCPss, and a biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC) encoding non-ribosomal peptide synthase (nrps). The divergently transcribed ropBss and LCPss along with predicted transcription start site (PLCPss, bent arrow) of LCPss are shown. The numbers below denote the nucleotide positions relative to the first nucleotide of the start codon of nrps-BGC. b The nucleotide sequence of the ropBss-LCPss intergenic region, coding sequence of LCPss, and corresponding predicted amino acid sequence of LCPss are shown. The ribosomal-binding sites (RBS) of LCPss and RopBss are denoted by arrows. c Analysis of nrps transcript levels in the indicated strains by qRT-PCR. d Addition of full-length synthetic LCPss activates nrps expression in LCPss inactivated mutant (LCPss*). The amino acid sequences of the synthetic LCPss variants used are shown (right). e qRT-PCR based nrps transcript level analyses in LCPss* mutant grown in spent medium from the indicated strains. f Cytosolic fluorescence corresponding to FITC-labeled LCPss indicative of the import of exogenous LCPss as assessed by fluorescence measurements. Unmodified or FITC-labeled LCPss was added at a final concentration of 1 µM to either WT or oligopeptide permease-inactivated mutant (∆opp). After 30 min incubation, fluorescence in the clarified cell lysates was measured using excitation and emission wavelengths of 480 nm and 520 nm, respectively. g Analysis of the binding between purified RopBss and fluoresceinated LCPss by fluorescence polarization (FP) assay. h Ability of LCPss or SCRA peptide to compete with the FITC-labeled LCPss–RopBss complex for binding. A preformed RopB (250 nM)-labeled LCPss (10 nM) complex was challenged with the indicated unlabeled peptides. i Nucleotide sequence of the identified RopBss binding site in LCPss promoter used in the DNA-binding studies is shown. j Summary of the affinity of different forms of RopBss to LCPss promoter as assessed by FP assays. k Proposed model for LCPss signaling. LCPss is produced, exported, and reinternalized into the cytosol. The recognition of LCPss by RopBss promotes high affinity interactions between RopBss and binding site in LCPss promoter, which leads to the upregulation of LCPss and NRPS-BGC. In (c, d, e, f), data are derived from three biological replicates and analyzed in duplicates. In (g, h), data are derived from three independent experiments. In (c–h), data graphed represent mean values ± s.e.m. P values in (c, d, e, f) were calculated by Kruskal-Wallis test. In (c), * - P = 0.0259, ** - P = 0.073. In (d), * - P = 0.014. In (e), * - P = 0.0114, ** - P = 0.0027. In (f), ** - P = 0.0016, **** - P < 0.0001. n.s not significant. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.