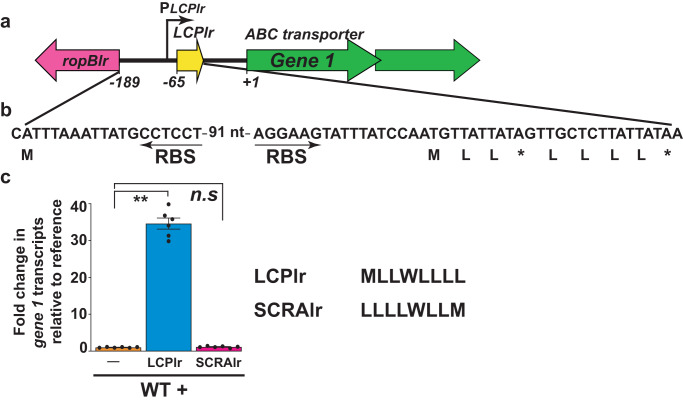
Fig. 6. LCP from a diverse species mediate intercellular signaling in Limosilactobacillus reuteri.
a Schematic representation of genetic elements in L. reuteri (lr) encoding ropBlr, LCPlr, ABC transporter (Gene 1). The ropBlr and LCPlr are divergently transcribed. The bent arrow above indicates the transcription start site of LCPlr. The numbers below denote the nucleotide positions relative to the first nucleotide of the start codon of gene 1. b The nucleotide sequence of the ropBlr-LCPlr intergenic region, coding sequence of LCPlr, and corresponding predicted amino acid sequence of LCPlr are shown. The ribosomal-binding sites (RBS) of LCPlr and RopBlr are marked by arrows. c Addition of synthetic LCPlr causes early induction of gene 1 expression in WT L. reuteri. Gene 1 transcript levels were assessed by qRT-PCR and the fold change in expression relative to unsupplemented growth (reference) is shown. In (c), data are derived from three biological replicates analyzed in duplicate and data graphed represent mean values ± s.e.m. P values in (c) were calculated by Kruskal-Wallis test. ** - P = 0.0024, n.s not significant. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.