Figure 4. Cellular and phenotypic alterations during therapy with DHODH Inhibitors.
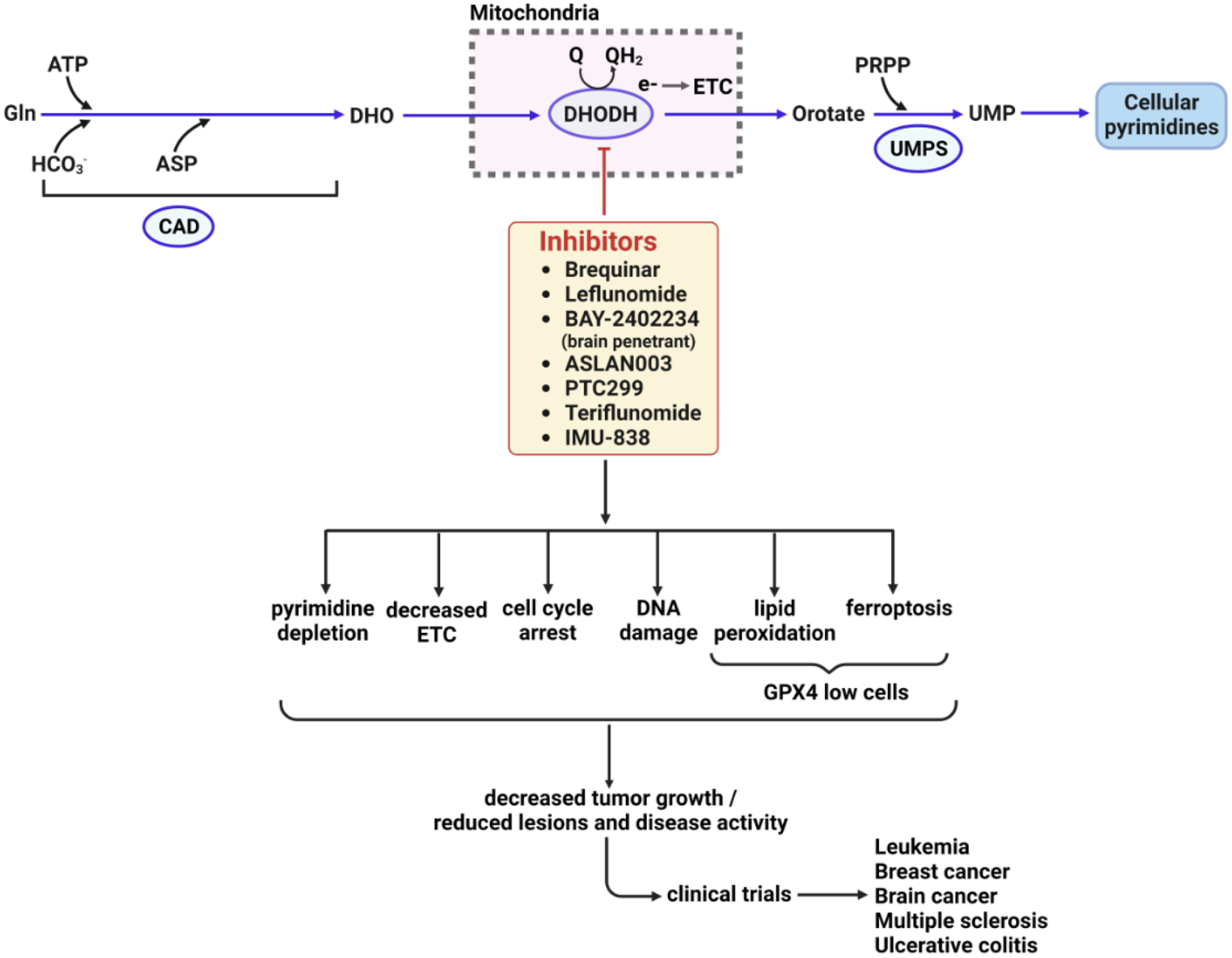
DHODH is necessary for the generation of cellular pyrimidine levels, and as such, its inhibitors have been long used to treat various autoimmune diseases, and are in clinical trials for cancer and immune disorders. A DHODH inhibitor quickly depletes cellular pyrimidine levels, forcing cells to limit the synthesis of RNA and DNA. Additionally, functional imbalance in ETC, cell cycle arrest, DNA damage, DNA replication stress could play critical roles in reducing tumor growth or inflammatory lesions. Furthermore, inhibition of DHODH might also increase mitochondrial lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis in GPX4low cancer cells and suppress GPX4low tumor growth [90]. DHO, dihydroorotate; UMP, uridine monophosphate; ETC, electron transport chain. GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4.
