Figure 3. Time-resolved correlation accounts for changes in dynamical stability across consciousness and propofol anesthesia.
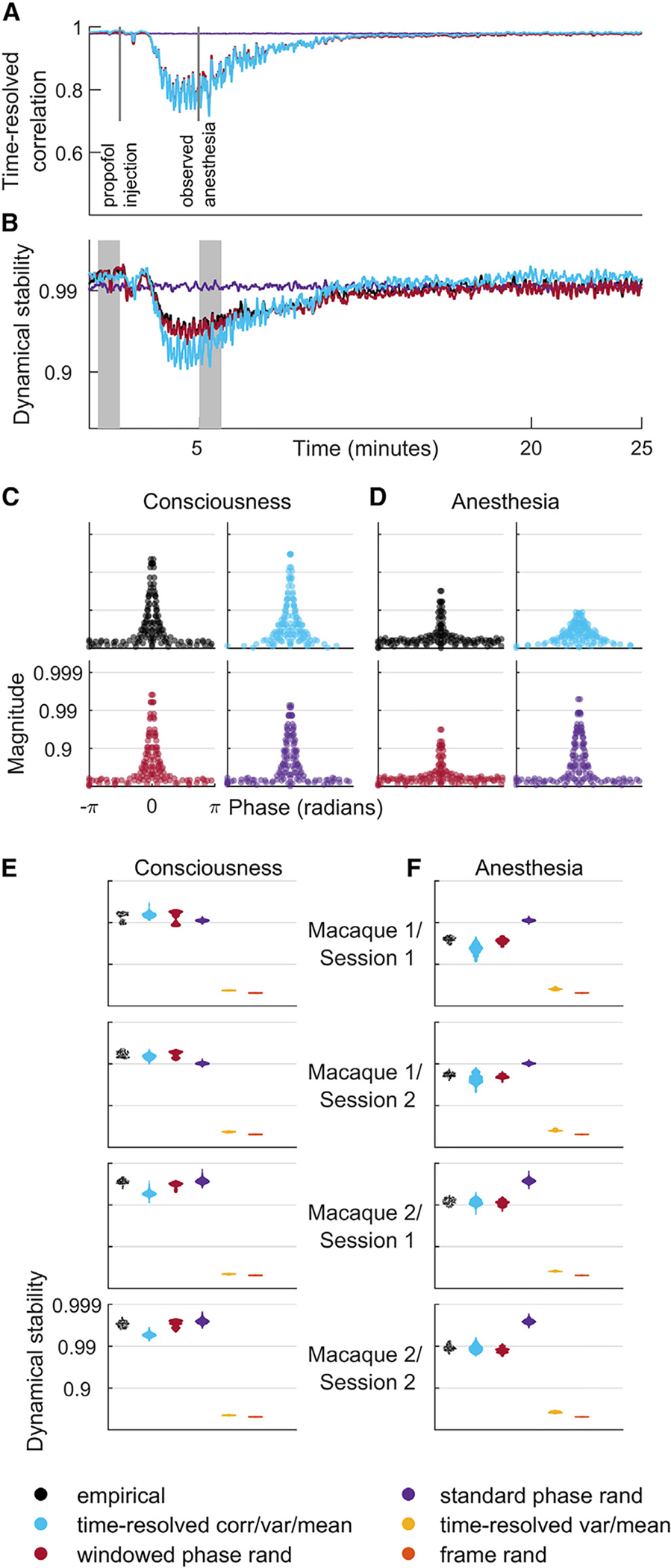
(A) Fluctuations of time-resolved correlation for model data of a representative electrocorticography recording.
(B) Dynamical stability index, the median value of the 5% largest eigenvalues, for the same recording. Note the strong correlation of time-resolved correlation with dynamical stability.
(C and D) Phase and magnitude of eigenvalues of a vector autoregressive model fit to a single window from periods of consciousness and anesthesia (shaded intervals in B, equivalent to intervals in Figures 1D–1G). Note the anesthesia-associated drop of dynamical stability in model data constrained by time-resolved correlation.
(E and F) Dynamical stability index across all empirical and model data, pooled over all recordings and averaged over all windows denoting periods of consciousness (E) and anesthesia (F).
Results for model data were derived using 50 samples for each model of each dataset. For completeness, Figures S5–S8 show individual results for all model datasets.
