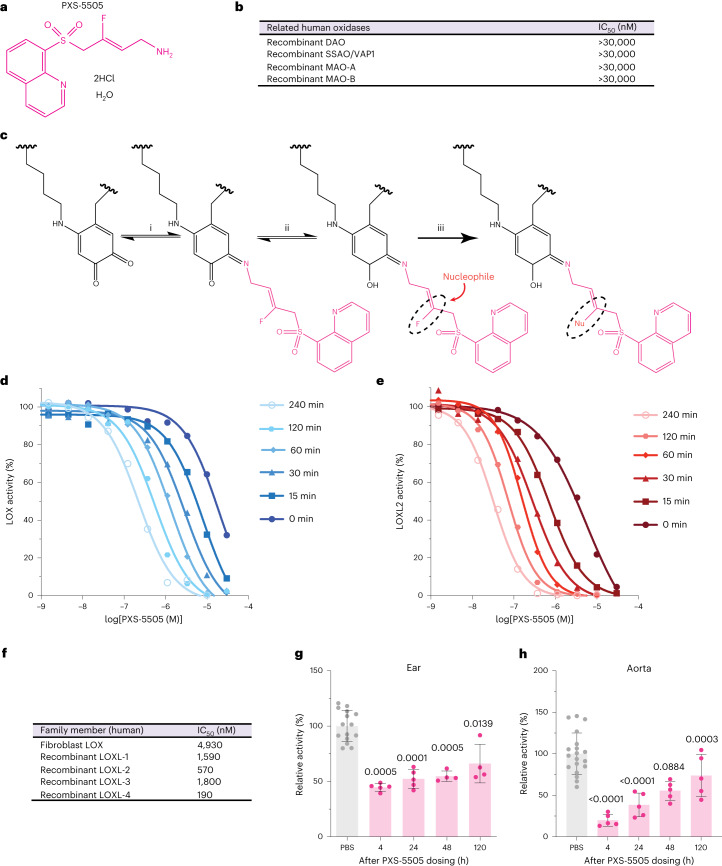
Fig. 2. PXS-5505 is a first-in-class pan-LOX inhibitor.
a, Chemical structure of PXS-5505. b, IC50 determination of PXS-5505 against other human amine oxidases: DAO, SSAO/VAP-1 and MAO-A and MAO-B. c, Proposed mechanism of lysyl oxidase inhibition by PXS-5505 through (i) initial binding to the LTQ complex in the enzymatic pocket to form a Schiff base, which then undergoes oxidation (ii) substitution of the fluorine with a nucleophilic amino acid (iii) formation of a covalently bound enzyme-inhibitor complex, resulting in irreversible loss of enzymatic activity. d, Representative plot of time-dependent inhibition of LOX specific activity showing increased potency with increased pre-incubation time, 0–240 min (n = 3 biologically independent samples). e, Representative plot of time-dependent inhibition of LOXL2 specific activity showing increased potency with increased pre-incubation time, 0–240 min (n = 3 biologically independent samples). f, IC50 values of PXS-5505 for each of the five lysyl oxidase family members. g, Lysyl oxidase family activity measured in the ear of rats following a single 30 mg kg−1 oral dosing of PXS-5505 n = 15 (PBS), 5 (4, 24 h), 4 (48, 120 h) biological independent samples. Data are presented as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed P value determined by unpaired, nonparametric t-test with a Mann–Whitney U-test correction (comparison to PBS control). h, Lysyl oxidase family activity measured in freshly excised aorta determined by fluorometric activity assay n = 19 (PBS), 5 (4–120 h) biological independent samples. Data presented as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed P value determined by unpaired, nonparametric t-test with a Mann–Whitney U-test correction (comparison to PBS control).