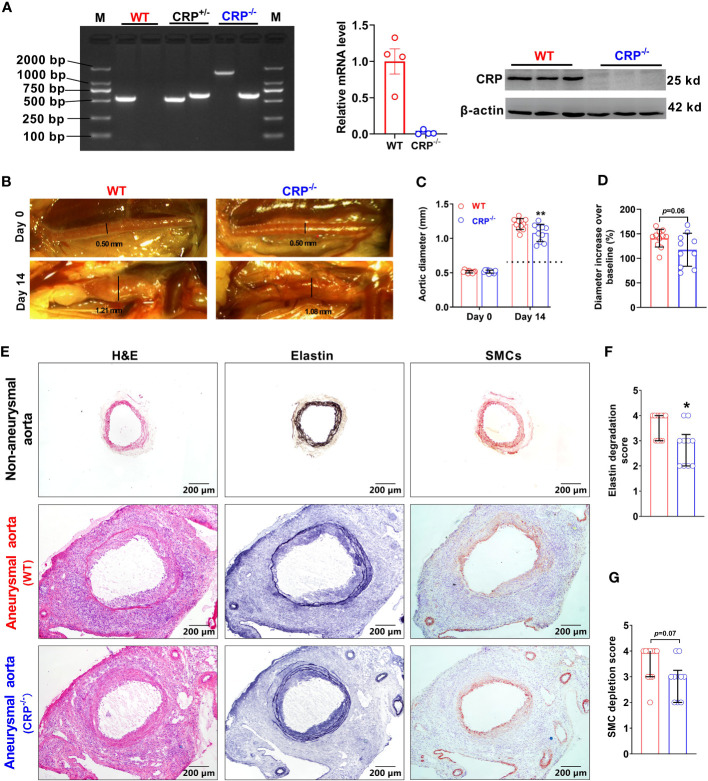
Figure 2.
CRP deficiency suppresses experimental aneurysmal dilation. (A): Phenotype identification of CRP deficient mice. Phenotyping for CRP homozygotes (CRP deficient mice: CRP-/-), CRP heterozygotes (CRP+/-) and wild type (WT) mice using PCR assay. CRP expression levels in the livers of CRP-/- and WT mice were determined via qRT-PCR and Western blotting analyses. (B): Representative photographic images for infrarenal aortas of wild type and CRP-/- mice prior to and 14 days after the elastase infusion. AAAs were induced in male CRP-/- and its wild type control mice using intra-aortic infusion of PPE. Influence on AAAs were assessed via in situ measurements of maximal infrarenal aortic diameters. Dotted line indicates aortic expansion even after PPE solvent (PBS) pressed infusion (about 0.8 mm in our lab) (C, D): Maximal infrarenal aortic external diameters presented as absolute diameter on days 0 (baseline) and 14 after PPE infusion (C) or the percentage of diameters over baseline (D). n=10-11 mice per group. Two-ANOVA followed by two group comparison, **p<0.01 compared to wild type mice at same timepoint (C). Student t-test, p=0.06 compared to wild type mice (D). (E): Representative aortic images for H&E (left panels), elastin via Elastic Van Gieson (middle panels), and SMCs via an anti-SMC α antibody immunostaining (right panels) from non-aneurysmal and aneurysmal (wild type and CRP-/-) mice. (F, G): Quantification of medial elastin degradation (F) and SMC depletion (G) scores (media and interquartile) of wild type and CRP-/- aneurysmal aortas. Nonparametric Mann-Whitney test, *p<0.05 compared to wild type mice.